Selective empathy involves showing understanding and compassion primarily toward those with whom one shares a close bond, such as pets, fostering deep emotional connections and trust. Universal empathy extends this compassion to all beings, encouraging broader kindness and ethical treatment beyond familiar circles. Balancing selective and universal empathy can enhance overall well-being and promote harmonious relationships within diverse environments.
Table of Comparison
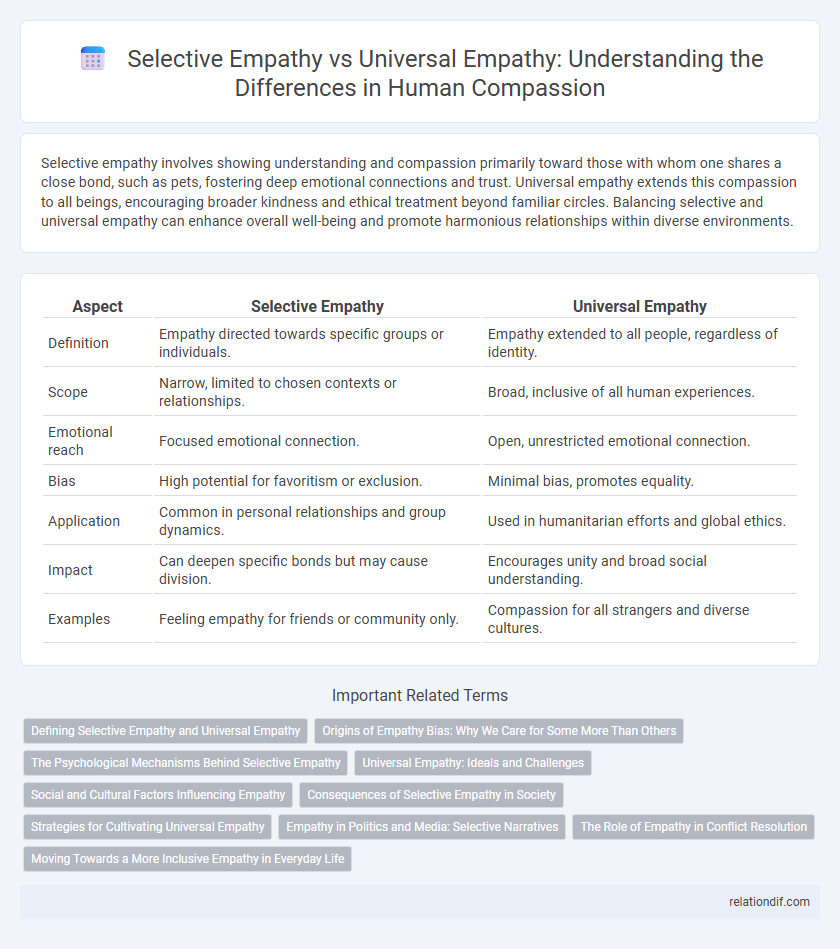
| Aspect | Selective Empathy | Universal Empathy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Empathy directed towards specific groups or individuals. | Empathy extended to all people, regardless of identity. |
| Scope | Narrow, limited to chosen contexts or relationships. | Broad, inclusive of all human experiences. |
| Emotional reach | Focused emotional connection. | Open, unrestricted emotional connection. |
| Bias | High potential for favoritism or exclusion. | Minimal bias, promotes equality. |
| Application | Common in personal relationships and group dynamics. | Used in humanitarian efforts and global ethics. |
| Impact | Can deepen specific bonds but may cause division. | Encourages unity and broad social understanding. |
| Examples | Feeling empathy for friends or community only. | Compassion for all strangers and diverse cultures. |
Defining Selective Empathy and Universal Empathy
Selective empathy involves the capacity to understand and share the feelings of specific individuals or groups based on shared characteristics, experiences, or identities, often leading to partial emotional engagement. Universal empathy extends this emotional understanding to all human beings regardless of background, promoting inclusivity and compassion beyond personal biases. Defining these concepts highlights the distinction between empathetic responses conditioned by affinity and those driven by a broader, unconditional concern for others.
Origins of Empathy Bias: Why We Care for Some More Than Others
Empathy bias originates from evolutionary and social factors shaping selective empathy, where individuals prioritize close relationships or in-group members due to shared experiences and genetic ties. Universal empathy, by contrast, expands concern beyond immediate circles, often nurtured by cultural norms, moral reasoning, and exposure to diverse perspectives. Neuroscientific studies reveal that mirror neuron activity intensifies for familiar or similar others, underpinning why we naturally care more for some while extending empathy universally requires conscious effort and societal influence.
The Psychological Mechanisms Behind Selective Empathy
Selective empathy arises from cognitive biases and in-group favoritism, where individuals prioritize emotional resonance with those who share similar traits or experiences. Neural mechanisms such as mirror neuron activation are modulated by social categorization processes, influencing empathy's intensity based on perceived group membership. This psychological filtering shapes selective empathy by enhancing emotional responses to familiar or relatable individuals while dampening reactions to out-group members.
Universal Empathy: Ideals and Challenges
Universal empathy embodies the ideal of extending understanding and compassion to all people regardless of background, fostering inclusivity and social cohesion. Challenges arise from the cognitive and emotional effort required to maintain this impartial perspective, often complicated by personal biases and societal divisions. Cultivating universal empathy demands intentional mindfulness and systemic support to overcome ingrained selective empathy tendencies tied to in-group favoritism.
Social and Cultural Factors Influencing Empathy
Social and cultural factors significantly shape selective empathy by conditioning individuals to empathize more with those who share similar identities, values, or group memberships. Universal empathy, in contrast, can be limited by cultural norms and socialization processes that emphasize in-group favoritism and out-group biases. Understanding the role of social identity theory, cultural narratives, and intergroup contact is critical for fostering broader empathetic responses that transcend group boundaries.
Consequences of Selective Empathy in Society
Selective empathy, where compassion is extended only to certain groups, fosters social division and reinforces systemic inequalities by marginalizing others. This partial perspective can lead to increased prejudice, discrimination, and social fragmentation, undermining social cohesion and collective well-being. In contrast, universal empathy promotes inclusivity, understanding, and cooperative problem-solving across diverse communities.
Strategies for Cultivating Universal Empathy
Strategies for cultivating universal empathy involve active perspective-taking and mindful listening to understand experiences beyond personal or cultural boundaries. Engaging with diverse narratives through literature, media, or dialogue fosters emotional connection to a broad range of human conditions. Practicing self-awareness of biases and committing to inclusive compassion enhances the ability to extend empathy universally.
Empathy in Politics and Media: Selective Narratives
Selective empathy in politics and media often amplifies partisan narratives by prioritizing the experiences of favored groups while marginalizing others, shaping public opinion through emotionally charged storytelling. Universal empathy challenges this by promoting understanding and compassion across diverse populations, encouraging policies that address broader social injustices objectively. Media framing plays a crucial role in either reinforcing selective empathy or fostering universal empathy, influencing societal cohesion and political polarization.
The Role of Empathy in Conflict Resolution
Selective empathy limits understanding by favoring certain groups, often intensifying biases and prolonging conflicts, whereas universal empathy promotes inclusivity and impartiality, fostering mutual respect and collaboration. In conflict resolution, universal empathy enables parties to acknowledge diverse perspectives, reducing hostility and facilitating constructive dialogue. Cultivating universal empathy enhances emotional intelligence and supports sustainable peacebuilding efforts across cultural and social divides.
Moving Towards a More Inclusive Empathy in Everyday Life
Selective empathy limits understanding to specific groups, often influenced by personal biases or social boundaries, while universal empathy embraces all individuals regardless of differences. Cultivating universal empathy requires actively recognizing shared human experiences and challenging prejudices that hinder emotional connection. Moving towards a more inclusive empathy in everyday life enhances social cohesion and fosters deeper, more meaningful interpersonal relationships across diverse communities.
Selective empathy vs universal empathy Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com