Self-empathy involves understanding and validating one's own emotions and needs, fostering personal insight and emotional resilience. Partner-empathy centers on recognizing and appreciating the feelings and perspectives of others, enhancing communication and connection within relationships. Balancing self-empathy and partner-empathy cultivates mutual respect and deepens emotional bonds.
Table of Comparison
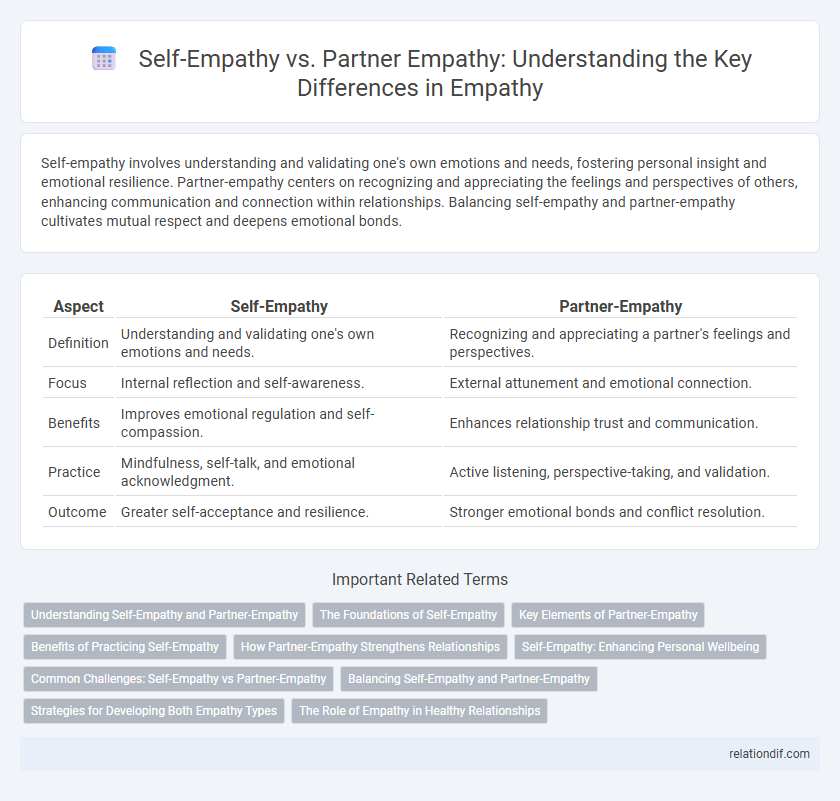
| Aspect | Self-Empathy | Partner-Empathy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Understanding and validating one's own emotions and needs. | Recognizing and appreciating a partner's feelings and perspectives. |
| Focus | Internal reflection and self-awareness. | External attunement and emotional connection. |
| Benefits | Improves emotional regulation and self-compassion. | Enhances relationship trust and communication. |
| Practice | Mindfulness, self-talk, and emotional acknowledgment. | Active listening, perspective-taking, and validation. |
| Outcome | Greater self-acceptance and resilience. | Stronger emotional bonds and conflict resolution. |
Understanding Self-Empathy and Partner-Empathy
Self-empathy involves recognizing and validating one's own emotions and needs, fostering deeper self-awareness and emotional regulation. Partner-empathy requires actively listening and responding to a partner's feelings and perspectives, which enhances mutual understanding and strengthens relational bonds. Balancing self-empathy with partner-empathy promotes healthier communication and emotional intimacy in relationships.
The Foundations of Self-Empathy
Self-empathy begins with recognizing and validating one's own emotions, fostering a nonjudgmental internal dialogue that enhances emotional clarity and resilience. Core foundations include mindfulness, self-awareness, and self-compassion, which enable individuals to process feelings without suppression or exaggeration. Developing self-empathy supports healthier relational dynamics by providing a stable emotional base from which partner-empathy can authentically emerge.
Key Elements of Partner-Empathy
Partner-empathy involves active listening, emotional attunement, and genuine validation of a partner's feelings, creating a safe and supportive environment for open communication. Key elements include recognizing verbal and non-verbal cues, suspending judgment, and responding with compassion and understanding to foster trust and deeper connection. Prioritizing partner-empathy enhances relationship resilience and promotes mutual emotional growth.
Benefits of Practicing Self-Empathy
Practicing self-empathy fosters emotional resilience by allowing individuals to genuinely understand and accept their own feelings, which reduces internal conflict and stress. This heightened self-awareness improves communication and nurtures healthier relationships by enabling more authentic and compassionate interactions with partners. Cultivating self-empathy also enhances mental well-being, promoting a balanced perspective that supports personal growth and emotional regulation.
How Partner-Empathy Strengthens Relationships
Partner-empathy fosters deeper emotional connection by enabling individuals to genuinely understand and validate their partner's feelings, which enhances trust and communication. Recognizing and responding to a partner's needs promotes conflict resolution and cultivates mutual support, essential for relationship resilience. Prioritizing partner-empathy over self-empathy encourages collaboration and shared emotional growth, strengthening relational bonds over time.
Self-Empathy: Enhancing Personal Wellbeing
Self-empathy involves recognizing and validating your own emotional experiences, fostering greater self-awareness and emotional resilience. Practicing self-empathy enhances personal wellbeing by reducing stress, promoting self-compassion, and improving mental health outcomes. Developing self-empathy serves as a foundation for healthier relationships and effective emotional regulation.
Common Challenges: Self-Empathy vs Partner-Empathy
Common challenges in self-empathy include overcoming internal criticism and recognizing one's own emotions without judgment, while partner-empathy often struggles with accurately interpreting the partner's feelings and maintaining emotional boundaries. Difficulty distinguishing personal feelings from those of a partner can blur empathetic responses, leading to misunderstandings. Cultivating clear self-awareness enhances both self-empathy and partner-empathy by promoting authentic emotional connection and reducing projection.
Balancing Self-Empathy and Partner-Empathy
Balancing self-empathy and partner-empathy requires recognizing and validating one's own emotions while simultaneously understanding and respecting the feelings of a partner. Effective empathy in relationships involves maintaining personal emotional boundaries to prevent self-neglect, ensuring mutual emotional support and connection without sacrificing individual well-being. Prioritizing both perspectives fosters healthier communication, deeper trust, and lasting emotional intimacy.
Strategies for Developing Both Empathy Types
Practicing mindful listening facilitates self-empathy by encouraging awareness of one's emotions without judgment, while partner-empathy deepens through reflective communication techniques such as paraphrasing and validating feelings. Developing emotional intelligence through regular self-reflection and journaling enhances recognition of personal and partner emotional states, promoting balanced empathy. Integrating perspective-taking exercises and establishing safe, open dialogue create an environment conducive to nurturing both self-empathy and partner-empathy simultaneously.
The Role of Empathy in Healthy Relationships
Self-empathy fosters emotional awareness and self-acceptance, enabling individuals to regulate their feelings and communicate authentically in relationships. Partner-empathy enhances connection by allowing one to understand and validate their partner's emotions, promoting trust and mutual respect. Together, self-empathy and partner-empathy create a balanced dynamic essential for emotional intimacy and conflict resolution in healthy relationships.
self-empathy vs partner-empathy Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com