A blended family combines children from previous relationships with new partners, forming a unique household dynamic that emphasizes cooperation and bonding among all members. Stepfamilies specifically highlight the role of a stepparent in nurturing and supporting children who are not biologically their own, fostering trust and emotional connection. Understanding the distinctions between blended families and stepfamilies helps address the challenges and strengths inherent in creating harmonious family relationships.
Table of Comparison
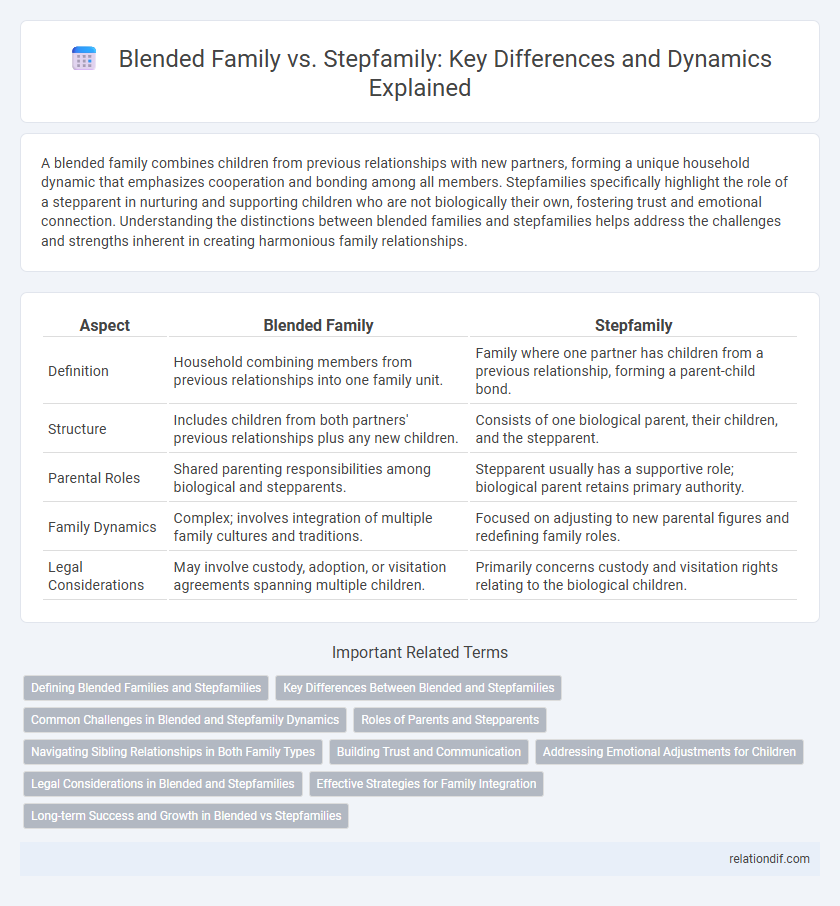
| Aspect | Blended Family | Stepfamily |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Household combining members from previous relationships into one family unit. | Family where one partner has children from a previous relationship, forming a parent-child bond. |
| Structure | Includes children from both partners' previous relationships plus any new children. | Consists of one biological parent, their children, and the stepparent. |
| Parental Roles | Shared parenting responsibilities among biological and stepparents. | Stepparent usually has a supportive role; biological parent retains primary authority. |
| Family Dynamics | Complex; involves integration of multiple family cultures and traditions. | Focused on adjusting to new parental figures and redefining family roles. |
| Legal Considerations | May involve custody, adoption, or visitation agreements spanning multiple children. | Primarily concerns custody and visitation rights relating to the biological children. |
Defining Blended Families and Stepfamilies
Blended families consist of partners who bring children from previous relationships into a new, shared household, creating a combined family unit. Stepfamilies specifically refer to families where one or both partners have children from prior relationships, and one or both form parental roles toward the other's children. Understanding these distinctions helps clarify the unique dynamics and challenges faced by each family structure.
Key Differences Between Blended and Stepfamilies
Blended families consist of partners who bring children from previous relationships, forming a new family unit that includes biological and non-biological siblings, while stepfamilies specifically refer to a parent and their stepchildren from a partner's previous relationship. Unlike stepfamilies, blended families often emphasize the integration of both partners' children into a shared household, creating complex relational dynamics and co-parenting challenges. Recognizing legal distinctions is crucial, as stepfamilies may have fewer automatic parental rights compared to blended family members who seek to establish joint guardianship.
Common Challenges in Blended and Stepfamily Dynamics
Blended and stepfamilies commonly face challenges such as navigating loyalty conflicts among children, establishing new parenting roles, and managing differences in family traditions. Communication barriers and unresolved emotions from previous family structures often contribute to tension and misunderstandings. Addressing these issues through open dialogue and family counseling can promote healthier dynamics and stronger relationships.
Roles of Parents and Stepparents
Blended families involve biological parents and their children forming a new family unit, where both parents often share active roles and responsibilities in parenting. In stepfamilies, stepparents assume supportive roles that may vary in involvement depending on the dynamics with stepchildren and biological parents. Effective communication and clear boundaries are essential for stepparents to integrate successfully and foster healthy relationships within these family structures.
Navigating Sibling Relationships in Both Family Types
Navigating sibling relationships in blended families often involves managing complex emotions and establishing new roles among stepsiblings who may have limited shared history. In stepfamilies, siblings might experience challenges related to loyalty conflicts and adjusting to new parental authorities, requiring clear communication and consistent boundaries. Successful relationships in both family types rely on empathy, patience, and the active creation of shared experiences to build trust and cohesion.
Building Trust and Communication
Building trust and communication in blended families involves integrating diverse family cultures and establishing consistent, open dialogue among all members. Stepfamilies benefit from intentional trust-building activities and clear communication channels that address unique emotional dynamics and role definitions. Emphasizing empathy and patience fosters a supportive environment where trust can grow steadily in both blended and stepfamily settings.
Addressing Emotional Adjustments for Children
Children in blended families often face complex emotional adjustments as they navigate relationships with new parental figures and step-siblings, requiring targeted support to foster trust and security. Stepfamilies benefit from establishing clear communication channels and consistent routines to help children adapt to changes and reduce feelings of confusion or divided loyalty. Providing access to counseling or family therapy can significantly ease emotional transitions and promote healthy bonding in both blended and stepfamily structures.
Legal Considerations in Blended and Stepfamilies
Legal considerations in blended and stepfamilies often revolve around custody rights, inheritance laws, and parental responsibilities, which can vary significantly depending on jurisdiction. Biological parents typically retain legal rights unless formal adoption occurs, making stepfamily members' legal status complex and requiring explicit legal actions to establish guardianship or custody. Addressing these issues proactively through legal documents such as wills, custody agreements, and powers of attorney helps ensure clarity and protection for all family members involved.
Effective Strategies for Family Integration
Blended families and stepfamilies require tailored integration strategies to foster unity and trust among members. Prioritizing open communication, establishing consistent routines, and respecting individual boundaries significantly enhance family cohesion. Implementing family counseling and shared activities promotes emotional bonding and smooth transitions, strengthening the family structure.
Long-term Success and Growth in Blended vs Stepfamilies
Blended families often demonstrate higher long-term success by fostering open communication and shared family traditions, which strengthens emotional bonds across biological and non-biological members. Stepfamilies may face unique challenges related to establishing trust and clear boundaries, but consistent family therapy and strong parental relationships contribute significantly to growth and stability. Research indicates that both family types benefit from deliberate efforts in conflict resolution and maintaining individual identities while nurturing collective unity.
blended family vs stepfamily Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com