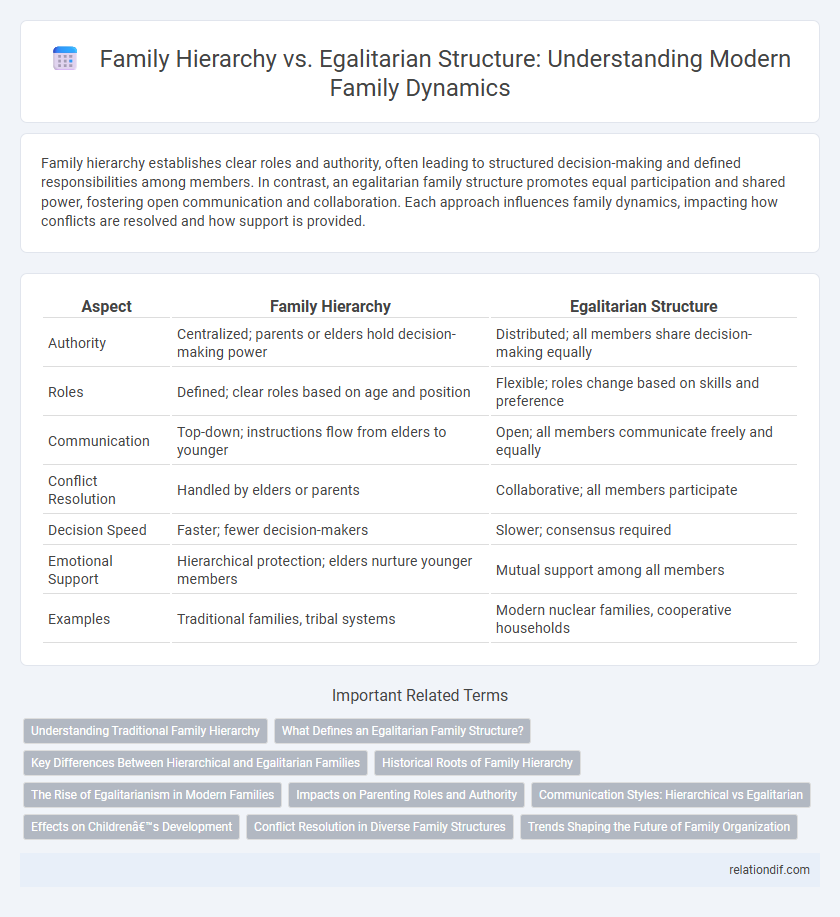
Family hierarchy establishes clear roles and authority, often leading to structured decision-making and defined responsibilities among members. In contrast, an egalitarian family structure promotes equal participation and shared power, fostering open communication and collaboration. Each approach influences family dynamics, impacting how conflicts are resolved and how support is provided.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Family Hierarchy | Egalitarian Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Authority | Centralized; parents or elders hold decision-making power | Distributed; all members share decision-making equally |
| Roles | Defined; clear roles based on age and position | Flexible; roles change based on skills and preference |
| Communication | Top-down; instructions flow from elders to younger | Open; all members communicate freely and equally |
| Conflict Resolution | Handled by elders or parents | Collaborative; all members participate |
| Decision Speed | Faster; fewer decision-makers | Slower; consensus required |
| Emotional Support | Hierarchical protection; elders nurture younger members | Mutual support among all members |
| Examples | Traditional families, tribal systems | Modern nuclear families, cooperative households |
Understanding Traditional Family Hierarchy
Traditional family hierarchy typically emphasizes clear roles, with parents holding authority over children and elders respected for their wisdom and decision-making power. This structure often reinforces generational obedience and defined responsibilities within households. Understanding these dynamics is essential to appreciating how cultural values shape family interactions and governance.
What Defines an Egalitarian Family Structure?
An egalitarian family structure is defined by shared decision-making power and equal responsibility among all members, regardless of age or gender. Roles within the family are flexible, promoting cooperation and mutual respect rather than rigid authority lines. This structure fosters open communication and prioritizes collective well-being over hierarchical control.
Key Differences Between Hierarchical and Egalitarian Families
Hierarchical families emphasize clearly defined roles and authority, with decision-making typically centralized in parental figures, fostering respect and obedience. Egalitarian families promote equal power distribution among members, encouraging shared responsibilities and collaborative decisions to enhance mutual respect and open communication. Key differences include authority structure, decision-making processes, and the dynamics of power and respect within family relationships.
Historical Roots of Family Hierarchy
Family hierarchy originated in patriarchal societies where authority was centralized around the eldest male, reflecting economic and social power dynamics. Historical structures placed fathers and eldest sons at the top, enforcing clear lines of authority and inheritance to preserve wealth and stability. Egalitarian family models emerged later, influenced by cultural shifts towards gender equality and shared responsibilities.
The Rise of Egalitarianism in Modern Families
Modern families increasingly adopt egalitarian structures, characterized by shared decision-making and balanced responsibilities among members. This shift challenges traditional family hierarchies where authority typically rests with a single parent or elder. Research highlights that egalitarian dynamics foster stronger emotional bonds and greater satisfaction within the family unit.
Impacts on Parenting Roles and Authority
In family hierarchies, parenting roles are clearly defined, often concentrating authority in the hands of parents, which fosters structured discipline and clear expectations for children. Egalitarian family structures promote shared decision-making between parents, encouraging collaboration and balanced authority that nurtures open communication and mutual respect. These differences significantly influence child development, with hierarchical families emphasizing obedience and egalitarian families prioritizing autonomy and emotional support.
Communication Styles: Hierarchical vs Egalitarian
Communication styles in hierarchical family structures often involve clear authority lines, with parents or elders directing conversations and decisions, emphasizing respect and obedience. In contrast, egalitarian families encourage open dialogue where all members, regardless of age, express opinions freely and participate equally in decision-making. This inclusive communication fosters mutual understanding, collaboration, and emotional support among family members.
Effects on Children’s Development
Family hierarchy often establishes clear roles and boundaries, which can promote discipline and a strong sense of responsibility in children. In contrast, an egalitarian family structure encourages open communication and shared decision-making, fostering independence and self-esteem. Research indicates that balanced approaches, combining structure with emotional support, tend to optimize children's social and cognitive development.
Conflict Resolution in Diverse Family Structures
Family hierarchy often establishes clear roles and authority, which can streamline conflict resolution but may suppress individual voices and lead to unresolved tensions. Egalitarian family structures promote open communication and equal participation, fostering collaborative problem-solving that respects diverse perspectives. Understanding these dynamics enhances conflict resolution strategies tailored to the unique needs of diverse family systems.
Trends Shaping the Future of Family Organization
Contemporary family organization increasingly shifts from traditional hierarchical models, where authority is typically vested in parental figures, towards egalitarian structures emphasizing shared decision-making and equal responsibilities among members. This trend aligns with evolving social values promoting gender equality, individual autonomy, and collaborative parenting, reflected in rising co-parenting arrangements and flexible family roles. Demographic data indicates a growing prevalence of dual-income households and multigenerational families adopting egalitarian principles, influencing child development outcomes and family cohesion in modern societies.
family hierarchy vs egalitarian structure Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com