Joint families foster close-knit relationships by sharing responsibilities, resources, and support among multiple generations under one roof, promoting a sense of belonging and collective well-being. Single-family households often offer greater privacy and autonomy, allowing members to make independent decisions and manage their routines more flexibly. Both family structures impact social dynamics and lifestyle choices, influencing emotional bonds and daily interactions.
Table of Comparison
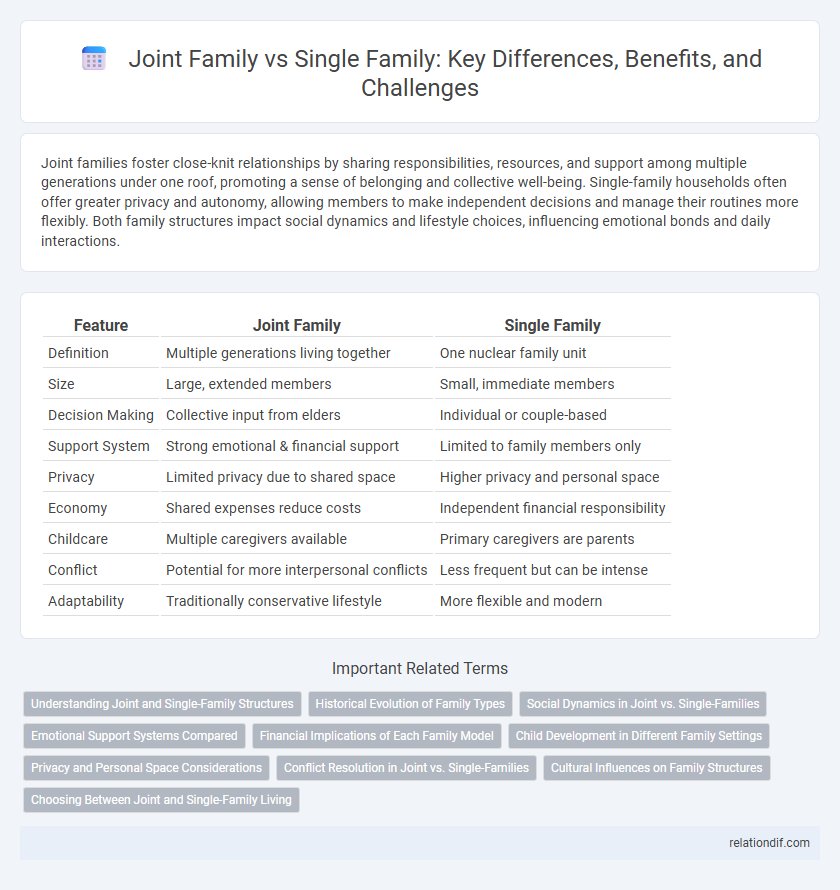
| Feature | Joint Family | Single Family |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Multiple generations living together | One nuclear family unit |
| Size | Large, extended members | Small, immediate members |
| Decision Making | Collective input from elders | Individual or couple-based |
| Support System | Strong emotional & financial support | Limited to family members only |
| Privacy | Limited privacy due to shared space | Higher privacy and personal space |
| Economy | Shared expenses reduce costs | Independent financial responsibility |
| Childcare | Multiple caregivers available | Primary caregivers are parents |
| Conflict | Potential for more interpersonal conflicts | Less frequent but can be intense |
| Adaptability | Traditionally conservative lifestyle | More flexible and modern |
Understanding Joint and Single-Family Structures
Joint family structures involve multiple generations living under one roof, sharing resources, responsibilities, and decision-making, which fosters strong familial bonds and collective support systems. Single-family households typically consist of nuclear units, emphasizing independence and privacy but sometimes lacking the extensive support network found in joint families. Understanding these structures reveals how cultural, economic, and social factors shape family dynamics, affecting emotional well-being and resource distribution.
Historical Evolution of Family Types
Joint families have historically been prevalent in agrarian and traditional societies, where extended kinship networks shared resources and responsibilities to ensure economic stability and social support. The rise of industrialization and urbanization in the 19th and 20th centuries prompted a shift toward nuclear or single-family households, prioritizing mobility, privacy, and individual economic independence. Contemporary family dynamics often reflect a blend of these models, influenced by cultural, economic, and demographic changes worldwide.
Social Dynamics in Joint vs. Single-Families
Joint families foster complex social dynamics with shared responsibilities and intergenerational interactions that enhance emotional support and collective decision-making. Single families tend to experience more autonomy and privacy but may face limited social resources and reduced daily interpersonal engagement. The contrast in social dynamics influences individual roles, communication patterns, and conflict resolution within each family structure.
Emotional Support Systems Compared
Joint families provide robust emotional support systems through shared responsibilities and constant companionship, fostering resilience in times of stress. Single-family units often rely on fewer emotional resources, intensifying the need for external social networks and professional support. Studies indicate that joint family members report higher levels of emotional security and collective problem-solving compared to their single-family counterparts.
Financial Implications of Each Family Model
Joint families benefit from pooled financial resources, reducing individual expenses through shared housing, utilities, and groceries, which often leads to greater economic stability and saving potential. In contrast, single-family households face higher per capita costs for housing, childcare, and daily necessities, increasing financial strain but offering more autonomy in budgeting and spending decisions. Financial planning in joint families requires coordination among members, while single families manage finances independently, affecting long-term investment and cash flow management.
Child Development in Different Family Settings
Children in joint families often benefit from diverse role models and shared responsibilities, promoting social skills and emotional resilience. Single-family settings provide children with focused parental attention and tailored guidance, enhancing individualized learning and emotional security. Both environments uniquely influence child development through varying degrees of social interaction and parental involvement.
Privacy and Personal Space Considerations
Joint families often face challenges in maintaining privacy and personal space due to shared living areas and multiple generations cohabiting, which can lead to limited individual autonomy. Single-family households generally provide greater privacy, allowing members to tailor their environment to personal needs and enjoy uninterrupted personal time. The trade-off between collective support in joint families and enhanced privacy in single-family setups significantly impacts daily family dynamics and individual well-being.
Conflict Resolution in Joint vs. Single-Families
Conflict resolution in joint families often involves collective decision-making and mediation by elders, fostering a supportive environment for addressing disputes; in contrast, single-family setups rely on direct communication between fewer members, allowing quicker but sometimes less balanced resolutions. Joint families benefit from diverse perspectives and shared responsibilities, which can diffuse tensions but may also prolong conflict due to larger group dynamics. Single-family units typically experience more autonomy in conflict management, yet may lack the broader social support found in joint family structures.
Cultural Influences on Family Structures
Cultural influences profoundly shape family structures, with joint families prevalent in collectivist societies emphasizing communal living, shared responsibilities, and strong intergenerational bonds. Single-family units are more common in individualistic cultures, prioritizing nuclear family privacy, autonomy, and economic independence. These cultural norms impact social roles, child-rearing practices, and support systems within various family models.
Choosing Between Joint and Single-Family Living
Choosing between joint and single-family living involves evaluating space, privacy, and support systems. Joint families offer shared responsibilities and emotional bonding, while single-family units provide independence and personalized environments. Financial considerations, cultural values, and individual preferences significantly influence this decision.
joint family vs single-family Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com