Parentification occurs when children take on adult responsibilities prematurely, leading to emotional strain and disrupted development. Infantilization, on the other hand, involves treating children as younger or less capable than they are, which can hinder independence and self-confidence. Recognizing and balancing these dynamics is crucial for healthy family relationships and fostering a child's emotional growth.
Table of Comparison
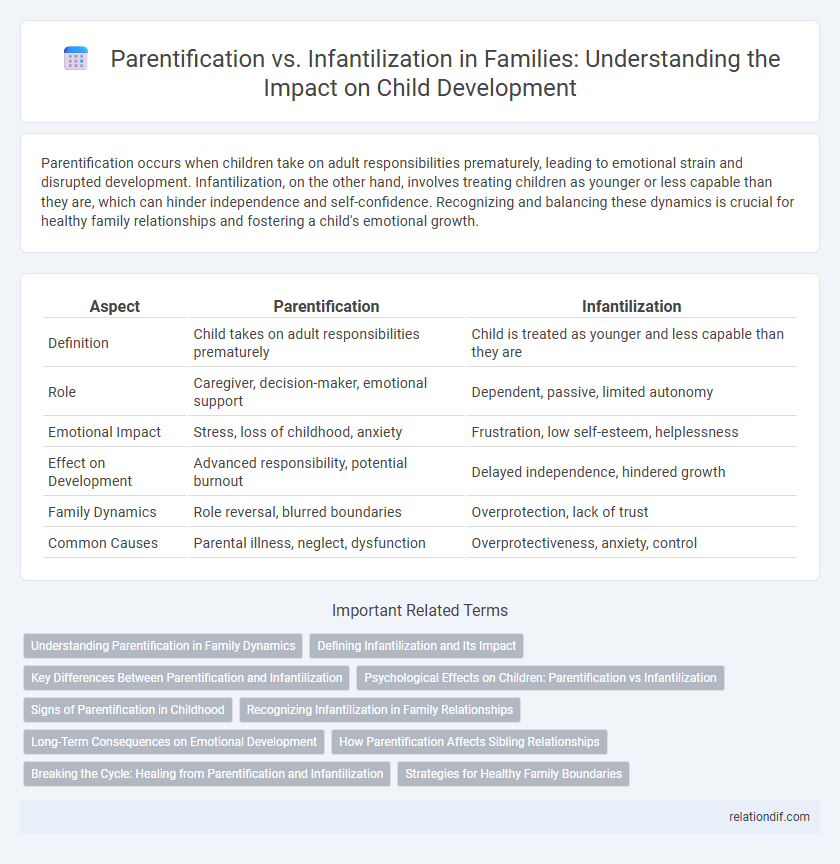
| Aspect | Parentification | Infantilization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Child takes on adult responsibilities prematurely | Child is treated as younger and less capable than they are |
| Role | Caregiver, decision-maker, emotional support | Dependent, passive, limited autonomy |
| Emotional Impact | Stress, loss of childhood, anxiety | Frustration, low self-esteem, helplessness |
| Effect on Development | Advanced responsibility, potential burnout | Delayed independence, hindered growth |
| Family Dynamics | Role reversal, blurred boundaries | Overprotection, lack of trust |
| Common Causes | Parental illness, neglect, dysfunction | Overprotectiveness, anxiety, control |
Understanding Parentification in Family Dynamics
Parentification occurs when children assume adult responsibilities, such as caregiving or emotional support, disrupting normal developmental roles within the family. This dynamic often leads to increased stress and anxiety in children, impairing their ability to form healthy boundaries and relationships later in life. Understanding the impact of parentification is crucial for fostering balanced family environments that support both child development and parental roles.
Defining Infantilization and Its Impact
Infantilization in family dynamics occurs when parents treat their children as younger or less capable than they truly are, inhibiting their emotional growth and independence. This behavior can lead to decreased self-esteem, increased dependency, and difficulty developing adult responsibilities in children. Understanding infantilization helps distinguish it from parentification, where children take on adult roles prematurely, highlighting contrasting but equally harmful family patterns.
Key Differences Between Parentification and Infantilization
Parentification involves a child taking on adult responsibilities and roles, often managing family dynamics or caregiving tasks, whereas infantilization occurs when parents overly protect or treat children as if they are incapable, hindering their independence. Parentification can lead to emotional stress and delayed childhood development, while infantilization may cause dependency issues and low self-esteem. Understanding these key differences helps to address and balance healthy boundaries in family relationships.
Psychological Effects on Children: Parentification vs Infantilization
Parentification often leads to increased anxiety, stress, and emotional burden as children assume adult responsibilities prematurely, impacting their social development and self-esteem. Infantilization, by contrast, can hinder a child's independence and self-confidence, causing feelings of helplessness and delayed emotional maturity. Both dynamics disrupt healthy psychological growth, increasing the risk of long-term relational and emotional difficulties.
Signs of Parentification in Childhood
Signs of parentification in childhood include excessive responsibility for household tasks, caring for siblings beyond age-appropriate levels, and prioritizing others' emotional needs over their own. Children showing parentification often exhibit maturity beyond their years, reduced time for play or socialization, and increased stress or anxiety related to family dynamics. Observing these behaviors can help identify imbalances where a child assumes adult-like roles prematurely.
Recognizing Infantilization in Family Relationships
Infantilization in family relationships occurs when parents excessively control or undermine a child's independence, treating them as much younger than their actual age. This behavior often leads to diminished self-esteem and stunted emotional development in the child. Recognizing signs such as overprotection, frequent decision-making on behalf of the child, and reluctance to allow age-appropriate responsibilities helps identify infantilization's negative impact.
Long-Term Consequences on Emotional Development
Parentification often leads to emotional burden and anxiety in adulthood, as the child assumes adult responsibilities prematurely, disrupting normal emotional development. Infantilization can result in dependency issues and poor self-regulation skills, causing difficulties in forming healthy relationships and self-esteem later in life. Both dynamics negatively impact emotional resilience, increasing the risk of chronic stress and mental health disorders.
How Parentification Affects Sibling Relationships
Parentification often disrupts sibling relationships by creating imbalanced roles where one child assumes parental responsibilities, leading to resentment or dependency among siblings. This role reversal can impede natural bonding and foster tension, as siblings may struggle with feelings of neglect or unfair expectations. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for addressing emotional needs and promoting healthier family interactions.
Breaking the Cycle: Healing from Parentification and Infantilization
Breaking the cycle of parentification and infantilization requires recognizing unhealthy role reversals within family dynamics and establishing clear boundaries. Therapeutic interventions often emphasize restoring balanced parent-child relationships, fostering emotional resilience, and promoting age-appropriate responsibilities. Empowering individuals to reclaim their authentic roles supports long-term healing and prevents repeating dysfunctional patterns in future generations.
Strategies for Healthy Family Boundaries
Establishing clear family roles and open communication helps prevent parentification and infantilization by promoting mutual respect and emotional balance. Consistent limits combined with empathy support individual autonomy while maintaining supportive connections among family members. Encouraging age-appropriate responsibilities fosters healthy development and reduces role confusion within the family system.
parentification vs infantilization Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com