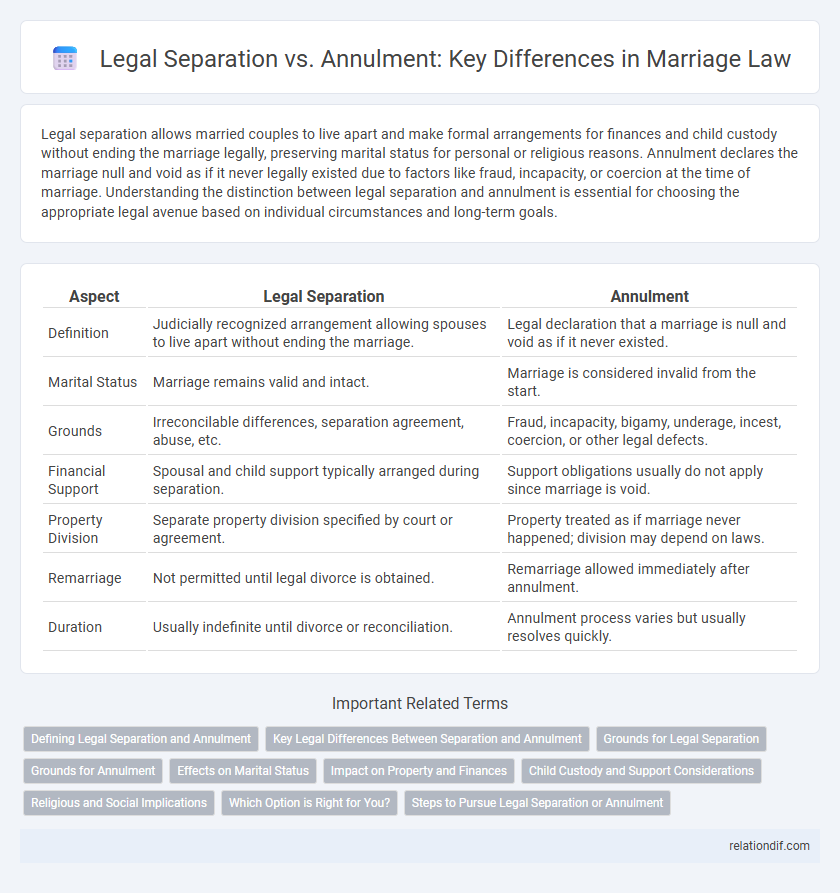
Legal separation allows married couples to live apart and make formal arrangements for finances and child custody without ending the marriage legally, preserving marital status for personal or religious reasons. Annulment declares the marriage null and void as if it never legally existed due to factors like fraud, incapacity, or coercion at the time of marriage. Understanding the distinction between legal separation and annulment is essential for choosing the appropriate legal avenue based on individual circumstances and long-term goals.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Legal Separation | Annulment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Judicially recognized arrangement allowing spouses to live apart without ending the marriage. | Legal declaration that a marriage is null and void as if it never existed. |
| Marital Status | Marriage remains valid and intact. | Marriage is considered invalid from the start. |
| Grounds | Irreconcilable differences, separation agreement, abuse, etc. | Fraud, incapacity, bigamy, underage, incest, coercion, or other legal defects. |
| Financial Support | Spousal and child support typically arranged during separation. | Support obligations usually do not apply since marriage is void. |
| Property Division | Separate property division specified by court or agreement. | Property treated as if marriage never happened; division may depend on laws. |
| Remarriage | Not permitted until legal divorce is obtained. | Remarriage allowed immediately after annulment. |
| Duration | Usually indefinite until divorce or reconciliation. | Annulment process varies but usually resolves quickly. |
Defining Legal Separation and Annulment
Legal separation is a court-approved arrangement allowing married couples to live apart and settle issues such as child custody, spousal support, and property division without dissolving the marriage. Annulment, in contrast, is a legal decree that declares a marriage null and void, as if it never legally existed, often based on factors like fraud, incapacity, or coercion. While legal separation maintains the marital status, annulment completely invalidates the marriage from the start.
Key Legal Differences Between Separation and Annulment
Legal separation allows couples to live apart while remaining legally married, preserving certain marital rights and obligations, such as spousal support and inheritance. Annulment declares a marriage null and void from the beginning, as if it never legally existed, based on factors like fraud, duress, or lack of consent. Unlike annulment, legal separation does not dissolve the marriage, so neither party can remarry unless they pursue a formal divorce.
Grounds for Legal Separation
Grounds for legal separation typically include cruelty, adultery, desertion, and habitual intoxication, providing a legal framework for spouses to live apart without dissolving the marriage. Unlike annulment, which declares a marriage null due to factors like fraud or incapacity, legal separation recognizes the validity of the marriage but allows for physical and financial separation. Courts require substantial evidence of these grounds to grant legal separation, ensuring protection and rights for both parties during the separation process.
Grounds for Annulment
Grounds for annulment include fraud, coercion, bigamy, underage marriage without proper consent, incest, and mental incapacity at the time of marriage. Legal separation does not require proving these conditions but focuses on the inability to live together peacefully. Annulment declares the marriage null and void, effectively stating it never legally existed.
Effects on Marital Status
Legal separation allows spouses to live apart without dissolving the marriage, so their marital status remains legally married, preserving rights such as inheritance and spousal support. Annulment declares the marriage null and void from the beginning, effectively erasing the marriage status as if it never existed, which impacts legal rights and obligations differently than divorce or separation. The choice between legal separation and annulment significantly affects legal documentation, tax filing status, and eligibility for remarriage.
Impact on Property and Finances
Legal separation allows spouses to divide assets and address alimony without dissolving the marriage, maintaining property rights as if still married. Annulment treats the marriage as if it never existed, often leading to the restoration of property to its pre-marriage state and nullification of financial obligations incurred during the union. Understanding the distinct financial implications is crucial for couples deciding between these two legal options.
Child Custody and Support Considerations
Legal separation and annulment both impact child custody and support, but legal separation typically establishes temporary arrangements recognized by the court, ensuring ongoing support and visitation rights. Annulment, declaring the marriage null from the start, may complicate custody decisions, especially if the child's legitimacy or parental rights are questioned. Courts prioritize the child's best interests, mandating support and stable custody regardless of the marital status resolution.
Religious and Social Implications
Legal separation allows married couples to live apart without dissolving the marriage, often respecting religious doctrines that prohibit divorce, thereby preserving social and spiritual status. Annulment declares a marriage null from the beginning, aligning with religious beliefs that a valid marriage never existed, which can affect community perceptions and personal identity within faith-based contexts. Both legal separation and annulment carry significant religious and social implications, influencing familial relationships, community acceptance, and individual rights.
Which Option is Right for You?
Choosing between legal separation and annulment depends on your unique circumstances and long-term goals. Legal separation allows couples to live apart while remaining legally married, often preserving benefits like health insurance and simplifying potential reconciliation. Annulment, which declares a marriage null and void as if it never existed, suits cases involving fraud, incapacity, or underage marriage, but typically requires specific legal grounds and time-sensitive filings.
Steps to Pursue Legal Separation or Annulment
To pursue legal separation, spouses must typically file a petition with the family court, outlining grounds such as irreconcilable differences, followed by mandatory mediation or counseling in some jurisdictions. Annulment requires proving specific legal grounds like fraud, incapacity, or bigamy, and submitting a petition within a statutory timeframe, often demanding substantial evidence and witness testimony. Both processes conclude with court hearings where a judge issues the final order, either granting separation with terms for division of assets and custody or declaring the marriage null and void.
Legal Separation vs Annulment Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com