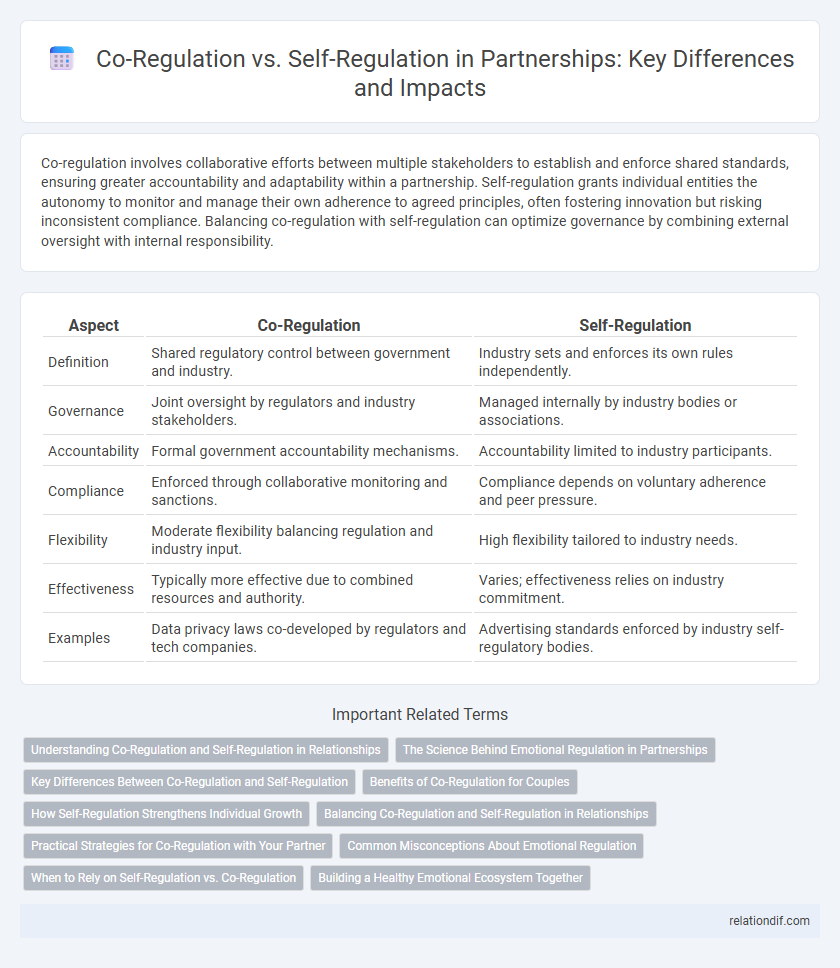
Co-regulation involves collaborative efforts between multiple stakeholders to establish and enforce shared standards, ensuring greater accountability and adaptability within a partnership. Self-regulation grants individual entities the autonomy to monitor and manage their own adherence to agreed principles, often fostering innovation but risking inconsistent compliance. Balancing co-regulation with self-regulation can optimize governance by combining external oversight with internal responsibility.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Co-Regulation | Self-Regulation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shared regulatory control between government and industry. | Industry sets and enforces its own rules independently. |
| Governance | Joint oversight by regulators and industry stakeholders. | Managed internally by industry bodies or associations. |
| Accountability | Formal government accountability mechanisms. | Accountability limited to industry participants. |
| Compliance | Enforced through collaborative monitoring and sanctions. | Compliance depends on voluntary adherence and peer pressure. |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility balancing regulation and industry input. | High flexibility tailored to industry needs. |
| Effectiveness | Typically more effective due to combined resources and authority. | Varies; effectiveness relies on industry commitment. |
| Examples | Data privacy laws co-developed by regulators and tech companies. | Advertising standards enforced by industry self-regulatory bodies. |
Understanding Co-Regulation and Self-Regulation in Relationships
Co-regulation in relationships involves partners mutually supporting each other's emotional and behavioral responses, creating a responsive feedback loop that enhances trust and connection. Self-regulation refers to an individual's ability to manage their emotions and impulses independently, contributing to relationship stability by preventing conflicts and fostering personal accountability. Effective partnerships balance co-regulation and self-regulation to promote resilience, communication, and emotional well-being.
The Science Behind Emotional Regulation in Partnerships
The science behind emotional regulation in partnerships highlights how co-regulation, the mutual management of emotions between partners, enhances relationship stability and satisfaction more effectively than self-regulation alone. Neurobiological studies reveal that co-regulation activates mirror neurons and oxytocin release, fostering empathy and trust essential for conflict resolution and emotional bonding. Research from the Journal of Social and Personal Relationships supports that couples practicing co-regulation exhibit lower cortisol levels and greater emotional resilience, underpinning healthier long-term partnerships.
Key Differences Between Co-Regulation and Self-Regulation
Co-regulation involves collaborative efforts between organizations and regulatory bodies to establish and enforce standards, whereas self-regulation relies solely on an organization's internal policies and procedures without external oversight. Key differences include the level of accountability, with co-regulation promoting shared responsibility and transparency, contrasted by self-regulation's emphasis on autonomy and internal governance. Co-regulation often results in stricter compliance due to external monitoring, while self-regulation provides greater flexibility but may risk inconsistent enforcement.
Benefits of Co-Regulation for Couples
Co-regulation enhances emotional connection by fostering mutual support and understanding between partners, leading to improved conflict resolution and relationship satisfaction. This shared regulatory process helps couples manage stress effectively, promoting healthier communication and emotional resilience. Couples engaging in co-regulation experience stronger bonding and increased trust compared to self-regulation, which often isolates emotional management.
How Self-Regulation Strengthens Individual Growth
Self-regulation empowers individuals to take ownership of their actions and decisions, fostering personal accountability and continuous improvement. By setting personal standards and reflecting on outcomes, individuals develop resilience and adaptability in dynamic environments. This intrinsic growth mechanism complements external frameworks by promoting ethical behavior and long-term success within partnerships.
Balancing Co-Regulation and Self-Regulation in Relationships
Balancing co-regulation and self-regulation in relationships requires clear communication and mutual understanding, ensuring that partners support each other's emotional needs without sacrificing personal autonomy. Effective partnerships leverage co-regulation to manage stress and navigate conflicts while maintaining self-regulation to foster individual growth and resilience. This dynamic interplay enhances relationship stability by creating a supportive environment where both collaborative and independent coping strategies coexist.
Practical Strategies for Co-Regulation with Your Partner
Effective co-regulation with your partner involves using practical strategies such as synchronized breathing exercises, active listening, and mindful touch to create emotional balance and mutual support. Establishing clear communication signals and shared rituals helps partners recognize stress responses early and respond collaboratively, strengthening their emotional connection. Regularly practicing these co-regulation techniques fosters resilience and improves relational stability by promoting empathy and reducing conflict.
Common Misconceptions About Emotional Regulation
Common misconceptions about emotional regulation often confuse co-regulation with self-regulation, overlooking the essential role of interpersonal support in managing emotions effectively. Co-regulation involves external guidance and responsiveness from a partner or caregiver, which helps individuals, especially children, develop intrinsic self-regulation skills over time. Successful partnerships recognize that emotional regulation is a dynamic process requiring both external co-regulation and internal self-regulation for optimal emotional health.
When to Rely on Self-Regulation vs. Co-Regulation
Self-regulation is most effective when industries possess strong internal expertise and shared values that enable consistent enforcement of standards without external oversight. Co-regulation becomes essential when complex regulatory environments demand collaboration between government authorities and private entities to ensure compliance and address gaps that self-regulation alone cannot manage. Companies should assess the maturity of their sector, stakeholder trust, and potential legal risks to determine the optimal balance between self-regulation and co-regulation frameworks.
Building a Healthy Emotional Ecosystem Together
Co-regulation involves partners actively supporting each other's emotional well-being, fostering mutual understanding and resilience within the relationship. Through shared emotional management, both individuals contribute to creating a stable and nurturing environment that enhances trust and empathy. This collaborative approach builds a healthy emotional ecosystem, promoting sustained connection and psychological safety.
co-regulation vs self-regulation Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com