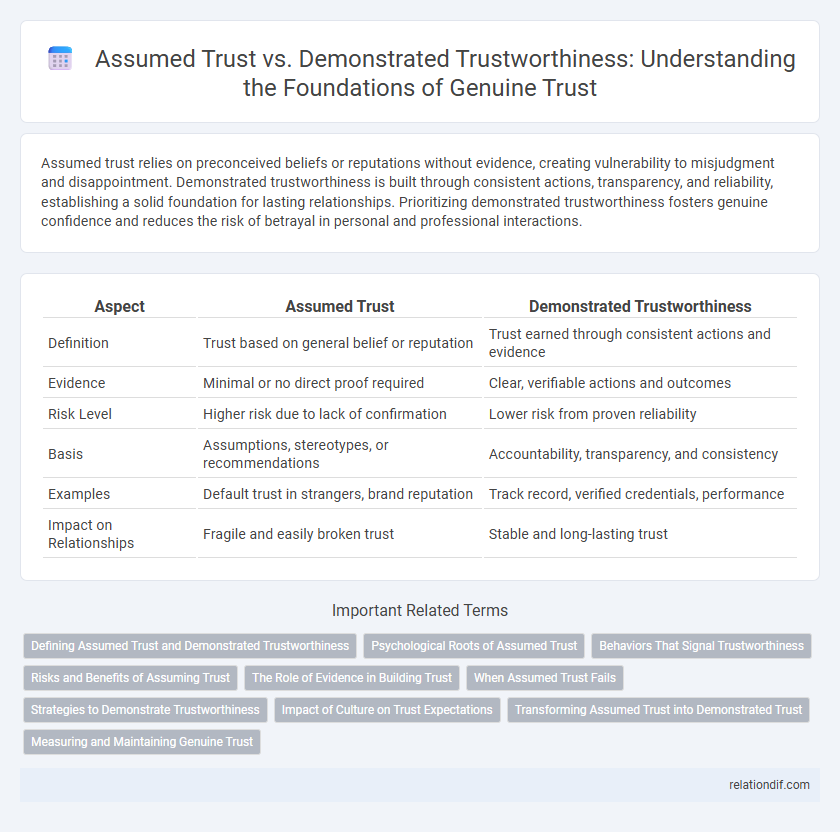
Assumed trust relies on preconceived beliefs or reputations without evidence, creating vulnerability to misjudgment and disappointment. Demonstrated trustworthiness is built through consistent actions, transparency, and reliability, establishing a solid foundation for lasting relationships. Prioritizing demonstrated trustworthiness fosters genuine confidence and reduces the risk of betrayal in personal and professional interactions.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Assumed Trust | Demonstrated Trustworthiness |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Trust based on general belief or reputation | Trust earned through consistent actions and evidence |
| Evidence | Minimal or no direct proof required | Clear, verifiable actions and outcomes |
| Risk Level | Higher risk due to lack of confirmation | Lower risk from proven reliability |
| Basis | Assumptions, stereotypes, or recommendations | Accountability, transparency, and consistency |
| Examples | Default trust in strangers, brand reputation | Track record, verified credentials, performance |
| Impact on Relationships | Fragile and easily broken trust | Stable and long-lasting trust |
Defining Assumed Trust and Demonstrated Trustworthiness
Assumed trust refers to the automatic confidence granted to an individual or entity based on reputation, role, or social norms without direct verification. Demonstrated trustworthiness is established through consistent, observable behavior and proven reliability over time. Understanding the distinction emphasizes the need for evidence-based trust in professional and personal relationships.
Psychological Roots of Assumed Trust
Assumed trust originates from innate psychological mechanisms such as the need for social bonding and cognitive heuristics that simplify complex social judgments. Humans often rely on familiarity, reputation, and social signals to make quick trust decisions without direct evidence of trustworthiness. This implicit trust serves as a foundational basis for forming initial interpersonal connections before demonstrated trustworthiness is established through consistent behavior.
Behaviors That Signal Trustworthiness
Behaviors that signal trustworthiness include consistent honesty, transparency in communication, and reliability in fulfilling commitments, which collectively foster assumed trust. Demonstrated trustworthiness goes beyond assumptions by showcasing accountability through actions such as admitting mistakes, delivering on promises, and maintaining confidentiality. These behaviors reinforce credibility and strengthen relationships, transforming assumed trust into enduring trust based on proven integrity.
Risks and Benefits of Assuming Trust
Assumed trust accelerates collaboration by reducing the need for exhaustive verification, but it introduces risks such as increased vulnerability to deception and security breaches. Demonstrated trustworthiness, established through consistent actions and verified credentials, mitigates these risks by providing reliable evidence of integrity and competence. Balancing assumed trust with mechanisms for verifying trustworthiness optimizes relationship management, enhancing efficiency while minimizing potential harm.
The Role of Evidence in Building Trust
Demonstrated trustworthiness relies on evidence such as consistent actions, transparent communication, and verified credentials that validate reliability and integrity. Assumed trust, often based on reputation or initial impressions, lacks this substantiation, making it more vulnerable to breach. The role of evidence is crucial in transforming assumed trust into durable confidence by providing measurable proof of trustworthiness.
When Assumed Trust Fails
When assumed trust fails, organizations face significant risks including data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage. Demonstrated trustworthiness, verified through transparent actions and consistent performance, reduces vulnerabilities by ensuring reliance is based on evidence rather than assumptions. Implementing rigorous verification protocols and continuous monitoring strengthens trust relationships and mitigates the consequences of misplaced confidence.
Strategies to Demonstrate Trustworthiness
Demonstrating trustworthiness requires consistent transparency, reliability, and effective communication to build and maintain confidence. Implementing strategies such as delivering on promises, openly sharing information, and showing accountability fosters a strong foundation of assumed trust. Trust is reinforced through actions that verify intentions, ultimately bridging the gap between assumed trust and proven credibility.
Impact of Culture on Trust Expectations
Cultural norms shape the expectations surrounding assumed trust and demonstrated trustworthiness, influencing how quickly and under what conditions trust is granted or earned. In high-context cultures, trust is often assumed based on social relationships and implicit understanding, whereas low-context cultures rely more heavily on explicit demonstration of reliability and competence. These differing trust paradigms affect cross-cultural communication, collaboration, and the establishment of effective partnerships.
Transforming Assumed Trust into Demonstrated Trust
Transforming assumed trust into demonstrated trust involves consistently aligning actions with promises and providing verifiable evidence of reliability. Organizations must implement transparent communication, uphold accountability standards, and deliver measurable results to validate initial trust assumptions. This process solidifies relationships by shifting perception from blind faith to confident assurance based on proven behavior.
Measuring and Maintaining Genuine Trust
Measuring genuine trust relies on consistent demonstration of reliability, transparency, and integrity over time rather than assumed trust based on reputation or initial impressions. Maintaining demonstrated trustworthiness involves continuous validation through measurable outcomes, feedback loops, and accountability mechanisms that reinforce credibility. Effective trust management prioritizes evidence-based interactions and clear communication to sustain authentic trust in relationships and organizations.
Assumed trust vs Demonstrated trustworthiness Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com