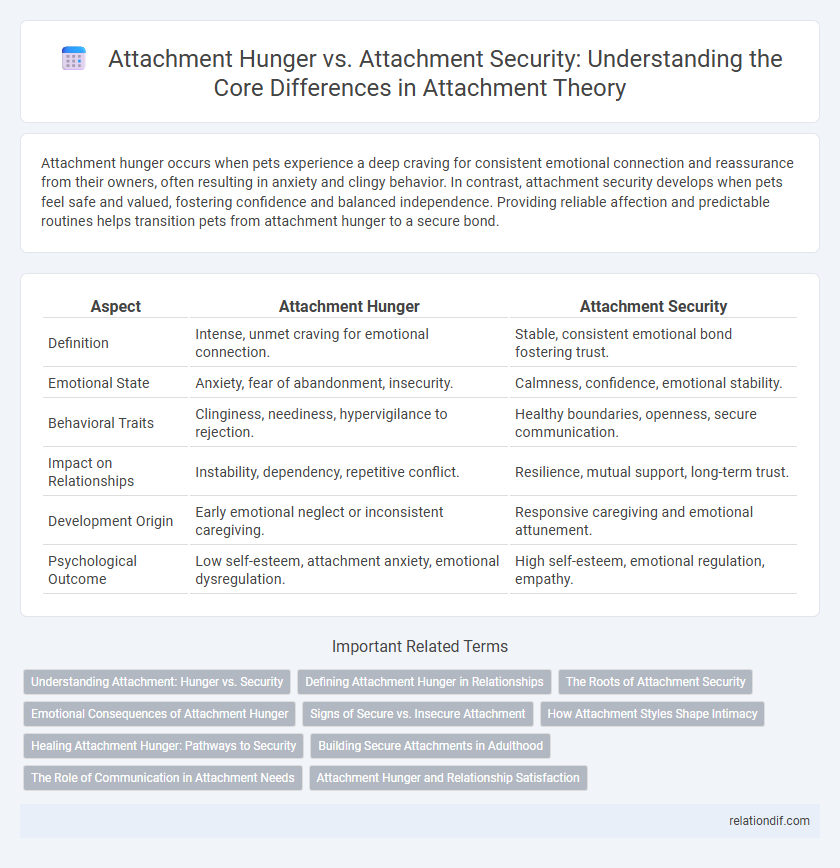
Attachment hunger occurs when pets experience a deep craving for consistent emotional connection and reassurance from their owners, often resulting in anxiety and clingy behavior. In contrast, attachment security develops when pets feel safe and valued, fostering confidence and balanced independence. Providing reliable affection and predictable routines helps transition pets from attachment hunger to a secure bond.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Attachment Hunger | Attachment Security |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Intense, unmet craving for emotional connection. | Stable, consistent emotional bond fostering trust. |
| Emotional State | Anxiety, fear of abandonment, insecurity. | Calmness, confidence, emotional stability. |
| Behavioral Traits | Clinginess, neediness, hypervigilance to rejection. | Healthy boundaries, openness, secure communication. |
| Impact on Relationships | Instability, dependency, repetitive conflict. | Resilience, mutual support, long-term trust. |
| Development Origin | Early emotional neglect or inconsistent caregiving. | Responsive caregiving and emotional attunement. |
| Psychological Outcome | Low self-esteem, attachment anxiety, emotional dysregulation. | High self-esteem, emotional regulation, empathy. |
Understanding Attachment: Hunger vs. Security
Attachment hunger reflects an intense craving for emotional connection and validation, often stemming from inconsistent caregiving and unmet emotional needs during early development. Attachment security emerges from reliable, responsive caregiving that fosters trust, emotional stability, and healthy relational bonds. Recognizing the distinctions between attachment hunger and attachment security is crucial for addressing emotional challenges and promoting psychological well-being.
Defining Attachment Hunger in Relationships
Attachment hunger in relationships refers to an intense longing for emotional connection and reassurance often stemming from unmet early attachment needs. This craving can lead to anxiety, clinginess, and difficulty trusting partners, contrasting with attachment security characterized by trust, stability, and comfort in intimacy. Understanding attachment hunger is crucial for addressing relational patterns and fostering healthier emotional bonds.
The Roots of Attachment Security
Attachment security originates from responsive and consistent caregiving that meets a child's emotional and physical needs, fostering trust and safety. Attachment hunger arises when these needs are unmet, causing distress and a persistent craving for connection and reassurance. Secure attachment lays the foundation for healthy emotional regulation and resilience throughout life.
Emotional Consequences of Attachment Hunger
Attachment hunger, characterized by a persistent lack of emotional connection, leads to increased anxiety, feelings of abandonment, and difficulties in forming trusting relationships. In contrast, attachment security fosters emotional stability, resilience, and healthy interpersonal bonds. The emotional consequences of attachment hunger often manifest in chronic loneliness, low self-esteem, and heightened sensitivity to rejection.
Signs of Secure vs. Insecure Attachment
Signs of secure attachment include consistent emotional availability, responsiveness, and trust between caregiver and child, fostering a strong sense of safety and confidence. Insecure attachment manifests through anxiety, avoidance, or ambivalence, often resulting in clinginess, withdrawal, or difficulty managing emotions. Attachment hunger reflects unmet needs for connection, amplifying signs of insecure attachment such as fear of abandonment and emotional distress.
How Attachment Styles Shape Intimacy
Attachment styles profoundly influence intimacy by shaping emotional availability and trust within relationships. Individuals with attachment security experience deeper connection and comfort with closeness, while those with attachment hunger often struggle with vulnerability, leading to heightened anxiety and fear of abandonment. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for fostering healthier, more secure attachments that enhance emotional intimacy.
Healing Attachment Hunger: Pathways to Security
Healing attachment hunger involves cultivating consistent, responsive caregiving that fosters trust and emotional safety, key components of attachment security. Therapeutic approaches like attachment-based therapy and emotionally focused therapy target unmet needs by promoting secure bonds and emotional regulation. Strengthening these pathways helps individuals transition from attachment hunger to secure and resilient relational patterns.
Building Secure Attachments in Adulthood
Attachment hunger, characterized by an intense craving for emotional connection, contrasts sharply with attachment security, which is marked by trust and comfort in relationships. Building secure attachments in adulthood involves consistent emotional availability, responsive communication, and vulnerability, fostering a reliable bond that meets deep relational needs. Therapeutic interventions like attachment-based therapy and mindful relationship practices play a crucial role in transforming attachment hunger into secure attachment patterns.
The Role of Communication in Attachment Needs
Communication plays a crucial role in differentiating attachment hunger from attachment security by conveying emotional availability and responsiveness between caregivers and children. Secure attachment is fostered through consistent, sensitive verbal and nonverbal interactions that validate the child's feelings and promote trust. In contrast, attachment hunger arises when communication is insufficient or erratic, leaving the child's attachment needs unmet and leading to feelings of insecurity.
Attachment Hunger and Relationship Satisfaction
Attachment hunger, characterized by an intense craving for emotional connection and validation, often leads to lower relationship satisfaction due to unmet needs and increased anxiety. Individuals experiencing attachment hunger may struggle with trust and feel persistent insecurity, negatively impacting intimacy and communication within relationships. Addressing attachment hunger through therapeutic interventions can enhance emotional regulation, fostering greater relationship satisfaction and stability.
attachment hunger vs attachment security Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com