Romantic attachment involves a deep emotional and physical connection characterized by passion, intimacy, and a desire for exclusivity with a partner. Platonic attachment, on the other hand, is founded on emotional closeness, trust, and mutual support without romantic or sexual intentions. Both forms of attachment fulfill essential human needs for security and belonging, but they differ in their expression and intensity within relationships.
Table of Comparison
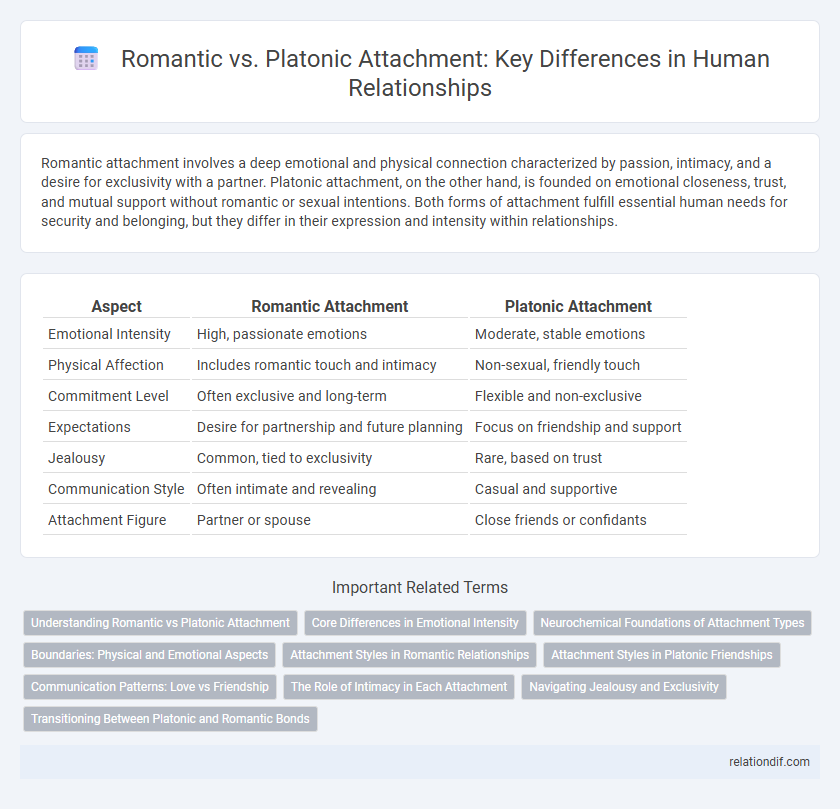
| Aspect | Romantic Attachment | Platonic Attachment |
|---|---|---|
| Emotional Intensity | High, passionate emotions | Moderate, stable emotions |
| Physical Affection | Includes romantic touch and intimacy | Non-sexual, friendly touch |
| Commitment Level | Often exclusive and long-term | Flexible and non-exclusive |
| Expectations | Desire for partnership and future planning | Focus on friendship and support |
| Jealousy | Common, tied to exclusivity | Rare, based on trust |
| Communication Style | Often intimate and revealing | Casual and supportive |
| Attachment Figure | Partner or spouse | Close friends or confidants |
Understanding Romantic vs Platonic Attachment
Romantic attachment involves deep emotional bonds characterized by passion, intimacy, and commitment, often activating the brain's reward system through oxytocin and dopamine. Platonic attachment centers on strong, non-sexual bonds based on trust, mutual respect, and emotional support, engaging areas related to social cognition and empathy. Understanding the neurochemical and psychological distinctions between romantic and platonic attachment provides insight into how different relationship types fulfill unique human needs.
Core Differences in Emotional Intensity
Romantic attachment involves intense emotional arousal driven by passion, desire, and exclusivity, often manifesting as deep longing and heightened physiological responses. Platonic attachment centers on stable, affectionate bonds characterized by companionship, trust, and mutual support without romantic or sexual desire. The core difference in emotional intensity lies in romantic attachment's combination of emotional passion and physical attraction versus platonic attachment's steady and non-sexual emotional connection.
Neurochemical Foundations of Attachment Types
Romantic attachment primarily involves heightened oxytocin and dopamine activity, reinforcing pair bonding and emotional intimacy, while platonic attachment relies more on vasopressin and endorphins that support trust and long-term social stability. Neuroimaging studies reveal distinct activation patterns in the brain's reward circuits, such as the ventral tegmental area and caudate nucleus, corresponding to varying attachment intensities. Understanding these neurochemical foundations elucidates how different attachment types influence human bonding behaviors and emotional regulation.
Boundaries: Physical and Emotional Aspects
Romantic attachment involves a blend of physical intimacy and deep emotional intertwining, requiring clear boundaries to maintain trust and mutual respect. Platonic attachment prioritizes emotional closeness with limited physical contact, emphasizing communication boundaries to foster a supportive, non-romantic connection. Both forms necessitate understanding and respecting personal limits to ensure healthy, balanced relationships.
Attachment Styles in Romantic Relationships
Romantic attachment in relationships often involves secure, anxious, avoidant, or disorganized attachment styles that influence emotional intimacy and trust levels between partners. Secure attachment fosters healthy communication and emotional regulation, while anxious attachment can lead to jealousy and dependency, and avoidant attachment typically results in emotional distancing. Understanding these attachment styles helps partners navigate conflicts and build stronger, more resilient romantic bonds compared to platonic attachments, which usually emphasize companionship and support without intense emotional dependency.
Attachment Styles in Platonic Friendships
Attachment styles in platonic friendships influence how individuals form and maintain close bonds, with secure attachment fostering trust and emotional support, while anxious attachment often leads to dependency and fear of rejection. Avoidant attachment in platonic relationships may cause emotional distance and reluctance to share personal feelings, limiting intimacy. Understanding these styles enhances communication and strengthens the resilience of platonic connections by addressing underlying emotional needs.
Communication Patterns: Love vs Friendship
Romantic attachment often involves emotionally charged communication patterns characterized by expressions of love, desire, and vulnerability, fostering intimacy and deeper emotional bonding. Platonic attachment, in contrast, emphasizes supportive, trust-based dialogue centered on mutual respect, shared interests, and encouragement without romantic or physical undertones. These distinct communication styles shape the emotional dynamics and expectations within romantic and platonic relationships.
The Role of Intimacy in Each Attachment
Romantic attachment is characterized by a deep emotional intimacy combined with physical closeness and passion, creating a bond that fosters exclusivity and emotional vulnerability. Platonic attachment centers on emotional intimacy without physical or romantic elements, relying on trust, mutual respect, and shared experiences to sustain the connection. In both attachments, intimacy facilitates secure bonding, but romantic intimacy often involves greater interdependence and attachment-related behaviors driven by desire.
Navigating Jealousy and Exclusivity
Romantic attachment often involves exclusivity and heightened sensitivity to jealousy due to the unique emotional and physical intimacy shared between partners. Platonic attachment, while deeply affectionate, generally lacks the same expectations of exclusivity, allowing for more flexible social boundaries. Navigating jealousy in romantic relationships requires clear communication and mutual trust, whereas in platonic bonds, understanding and respect for individual friendships help maintain harmony.
Transitioning Between Platonic and Romantic Bonds
Transitioning between platonic and romantic bonds involves navigating shifts in emotional intimacy and expectations, where trust and communication become essential to redefining the relationship dynamics. Neurochemical changes such as increased oxytocin and dopamine levels often accompany romantic attachment, distinguishing it from the stable, companionship-focused nature of platonic connections. Managing boundaries and recognizing evolving feelings help individuals maintain mutual respect while exploring deeper romantic commitment within a previously platonic relationship.
Romantic attachment vs platonic attachment Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com