Attachment security in pets fosters trust, confidence, and a sense of safety, leading to healthier emotional and behavioral outcomes. In contrast, attachment insecurity can result in anxiety, clinginess, or avoidance, negatively impacting the pet's well-being and their relationship with their owner. Secure attachments promote positive interactions and resilience, while insecure attachments may trigger stress and behavioral challenges.
Table of Comparison
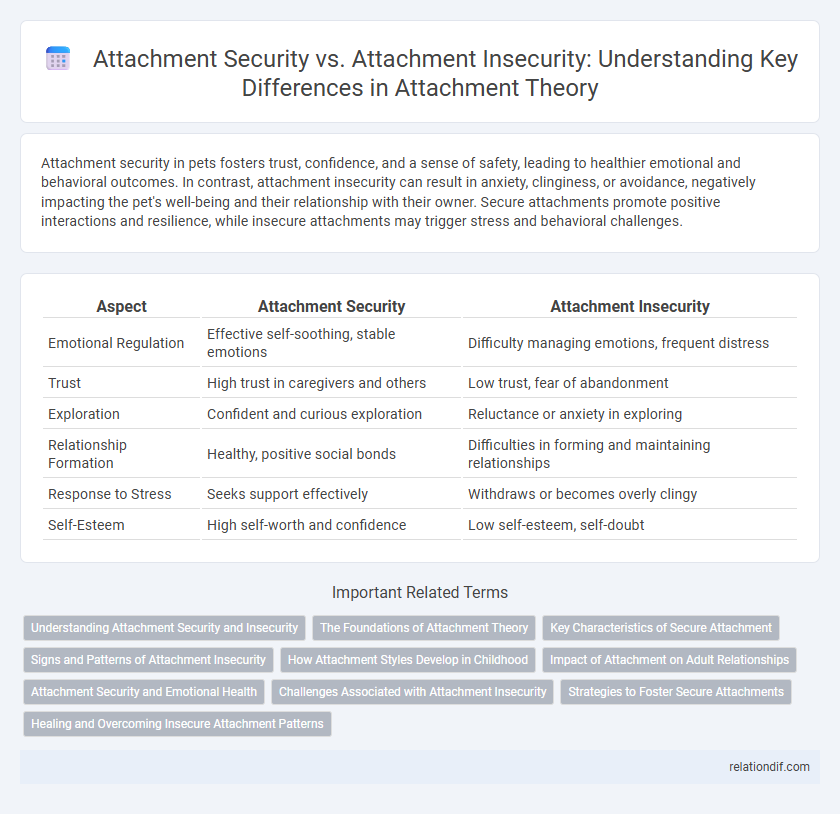
| Aspect | Attachment Security | Attachment Insecurity |
|---|---|---|
| Emotional Regulation | Effective self-soothing, stable emotions | Difficulty managing emotions, frequent distress |
| Trust | High trust in caregivers and others | Low trust, fear of abandonment |
| Exploration | Confident and curious exploration | Reluctance or anxiety in exploring |
| Relationship Formation | Healthy, positive social bonds | Difficulties in forming and maintaining relationships |
| Response to Stress | Seeks support effectively | Withdraws or becomes overly clingy |
| Self-Esteem | High self-worth and confidence | Low self-esteem, self-doubt |
Understanding Attachment Security and Insecurity
Attachment security is characterized by trust, effective emotional regulation, and a positive view of self and others, which fosters healthy interpersonal relationships. Attachment insecurity manifests as anxiety, avoidance, or disorganization, often rooted in inconsistent caregiving and leading to difficulties in emotional regulation and relationship stability. Understanding attachment security and insecurity is essential for identifying behavioral patterns and developing therapeutic interventions that promote emotional resilience and relational well-being.
The Foundations of Attachment Theory
Attachment security is characterized by consistent, sensitively attuned caregiving that fosters trust and emotional regulation in children, forming the core foundation of Bowlby's Attachment Theory. In contrast, attachment insecurity arises from inconsistent or neglectful caregiving, leading to anxiety, avoidance, or ambivalence in relationships. These early attachment patterns fundamentally influence an individual's social and emotional development throughout life.
Key Characteristics of Secure Attachment
Secure attachment is characterized by consistent responsiveness, emotional availability, and reliable support from caregivers, fostering trust and safety in relationships. Children with secure attachment exhibit effective emotion regulation, confidence in exploring their environment, and a positive internal working model of self and others. These key traits contribute to healthier social and emotional development, enhancing resilience and interpersonal competence throughout life.
Signs and Patterns of Attachment Insecurity
Attachment insecurity is characterized by patterns such as avoidance, anxiety, and ambivalence, often manifesting as difficulty trusting others, fear of abandonment, and inconsistent emotional responses. Signs include reluctance to form close relationships, excessive clinginess, or withdrawal during stress, reflecting maladaptive coping strategies linked to early relational experiences. These behaviors contrast with secure attachment, where individuals show comfort with intimacy and resilience in interpersonal challenges.
How Attachment Styles Develop in Childhood
Attachment styles develop in childhood through interactions with primary caregivers, where consistent responsiveness fosters secure attachment and inconsistent or neglectful care leads to attachment insecurity. Secure attachment forms when caregivers reliably meet emotional and physical needs, promoting trust and healthy emotional regulation. In contrast, attachment insecurity arises from unpredictability or rejection, resulting in anxiety, avoidance, or disorganized attachment patterns.
Impact of Attachment on Adult Relationships
Attachment security in adult relationships fosters trust, emotional intimacy, and effective communication, leading to stable and supportive partnerships. Attachment insecurity often results in anxiety, avoidance, and challenges in forming close bonds, which can cause relational conflicts and decreased satisfaction. Studies show secure attachment correlates with higher relationship quality and resilience, while insecure attachment increases the risk of maladaptive behaviors and emotional distress.
Attachment Security and Emotional Health
Attachment security fosters emotional health by promoting trust, self-esteem, and effective emotion regulation in relationships. Individuals with secure attachments exhibit resilience to stress and develop healthy interpersonal connections, contributing to overall psychological well-being. Strong attachment security supports adaptive coping mechanisms and reduces vulnerability to anxiety and depression.
Challenges Associated with Attachment Insecurity
Attachment insecurity often results in difficulties forming stable relationships due to fear of abandonment and mistrust. Individuals with attachment insecurity may experience heightened anxiety, emotional dysregulation, and challenges in effectively communicating their needs. These issues can lead to impaired social functioning and increased vulnerability to mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety.
Strategies to Foster Secure Attachments
Fostering secure attachments involves consistent responsiveness and emotional availability, which help build trust and safety in relationships. Caregivers can promote attachment security by engaging in sensitive and attuned interactions that validate feelings and support exploration. Establishing predictable routines and demonstrating reliable support are key strategies to reduce attachment insecurity and encourage emotional resilience.
Healing and Overcoming Insecure Attachment Patterns
Healing insecure attachment patterns involves building trust through consistent, empathetic interactions that promote emotional safety and regulation. Therapeutic approaches like cognitive-behavioral therapy and attachment-based therapy help individuals reframe negative beliefs and develop secure relational behaviors. Developing mindfulness and self-compassion further supports overcoming attachment insecurity by fostering self-awareness and emotional resilience.
Attachment security vs attachment insecurity Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com