Attachment wounds occur when early relationships fail to provide consistent care and emotional safety, leading to feelings of insecurity and mistrust. Attachment repairs involve therapeutic interventions and nurturing interactions that rebuild trust, fostering emotional regulation and secure bonds. Healing attachment wounds through repair processes promotes resilience and healthier relationships throughout life.
Table of Comparison
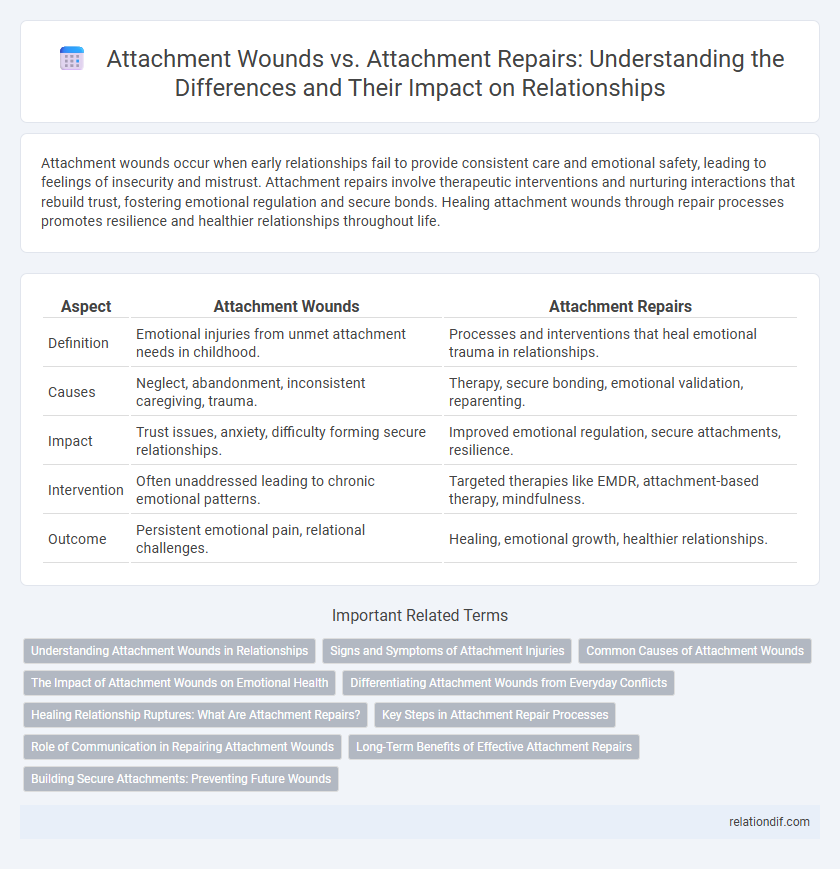
| Aspect | Attachment Wounds | Attachment Repairs |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Emotional injuries from unmet attachment needs in childhood. | Processes and interventions that heal emotional trauma in relationships. |
| Causes | Neglect, abandonment, inconsistent caregiving, trauma. | Therapy, secure bonding, emotional validation, reparenting. |
| Impact | Trust issues, anxiety, difficulty forming secure relationships. | Improved emotional regulation, secure attachments, resilience. |
| Intervention | Often unaddressed leading to chronic emotional patterns. | Targeted therapies like EMDR, attachment-based therapy, mindfulness. |
| Outcome | Persistent emotional pain, relational challenges. | Healing, emotional growth, healthier relationships. |
Understanding Attachment Wounds in Relationships
Attachment wounds in relationships stem from early experiences of emotional neglect, abandonment, or inconsistent caregiving, leading to difficulties in trust and intimacy. These wounds manifest as anxiety, fear of rejection, or avoidance, significantly impacting adult relationship dynamics and emotional regulation. Recognizing and addressing attachment wounds through therapeutic interventions fosters healthier connections and promotes emotional resilience.
Signs and Symptoms of Attachment Injuries
Attachment wounds manifest through symptoms such as trust issues, emotional withdrawal, and heightened anxiety in relationships, reflecting early disruptions in bonding. Signs of attachment injuries often include difficulty in emotional regulation, fear of abandonment, and recurring patterns of relational conflict. Effective attachment repairs are indicated by improved communication, increased emotional responsiveness, and the development of secure trust between individuals.
Common Causes of Attachment Wounds
Attachment wounds often stem from early emotional neglect, inconsistent caregiving, or traumatic separation during childhood. These experiences disrupt secure bonding and can result in difficulties with trust, emotional regulation, and forming healthy relationships. Recognizing these common causes is essential for addressing and facilitating effective attachment repairs.
The Impact of Attachment Wounds on Emotional Health
Attachment wounds significantly undermine emotional health by fostering deep-seated feelings of insecurity, mistrust, and low self-worth. Persistent unresolved attachment trauma often leads to chronic anxiety, depression, and difficulty in establishing healthy relational boundaries. Effective attachment repairs, such as therapeutic interventions and secure relational engagements, are crucial for restoring emotional resilience and fostering psychological well-being.
Differentiating Attachment Wounds from Everyday Conflicts
Attachment wounds stem from deep disruptions in the caregiver-child bond, causing lasting emotional pain and mistrust, whereas everyday conflicts are typically surface-level disagreements without significant impact on attachment security. These wounds manifest as patterns of anxiety, avoidance, or disorganized behavior linked to early relational trauma, contrasting with normal developmental challenges. Understanding this distinction is crucial for targeted therapeutic interventions that aim to repair attachment injuries rather than simply resolve minor disputes.
Healing Relationship Ruptures: What Are Attachment Repairs?
Attachment repairs refer to the processes involved in healing relationship ruptures by restoring trust and emotional security between partners. These repairs include open communication, acknowledging mistakes, and empathetic responsiveness, which help dissolve attachment wounds such as feelings of abandonment or rejection. Effective attachment repairs strengthen the bond, promoting resilience and deeper intimacy in relationships.
Key Steps in Attachment Repair Processes
Attachment repair processes involve recognizing attachment wounds caused by neglect or emotional injury, fostering open communication to express feelings and needs. Key steps include validating the partner's experiences, promoting empathy through active listening, and collaboratively developing trust-building behaviors. Consistent emotional responsiveness and mutual support are essential to healing attachment wounds and strengthening relational security.
Role of Communication in Repairing Attachment Wounds
Effective communication plays a crucial role in repairing attachment wounds by fostering trust and emotional safety between individuals. Open, empathetic dialogue helps identify underlying issues, validate feelings, and promote mutual understanding essential for healing relational rifts. Consistent, transparent communication rebuilds secure attachment patterns, restoring connection and resilience in relationships.
Long-Term Benefits of Effective Attachment Repairs
Effective attachment repairs facilitate secure emotional bonds by restoring trust and promoting resilience in relationships. Consistent repair efforts reduce the risk of chronic attachment wounds, leading to improved mental health and relational satisfaction over time. Long-term benefits include enhanced emotional regulation, greater intimacy, and stronger conflict resolution skills.
Building Secure Attachments: Preventing Future Wounds
Building secure attachments involves consistent emotional responsiveness that fosters trust and safety, reducing the likelihood of attachment wounds. Early relational experiences that address and repair misattunements promote resilience and emotional regulation, preventing the perpetuation of insecure attachment patterns. Effective attachment repairs create a foundation for healthy interpersonal connections and mitigate future emotional trauma.
Attachment Wounds vs Attachment Repairs Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com