Avoidant attachment in pets is characterized by a tendency to maintain emotional distance and appear indifferent to their owner's presence, often as a defense mechanism against rejection. Disorganized attachment presents as inconsistent and unpredictable behaviors, reflecting confusion and anxiety in response to the caregiver's actions. Understanding these attachment styles helps pet owners tailor their approach to foster a secure and trusting bond with their pets.
Table of Comparison
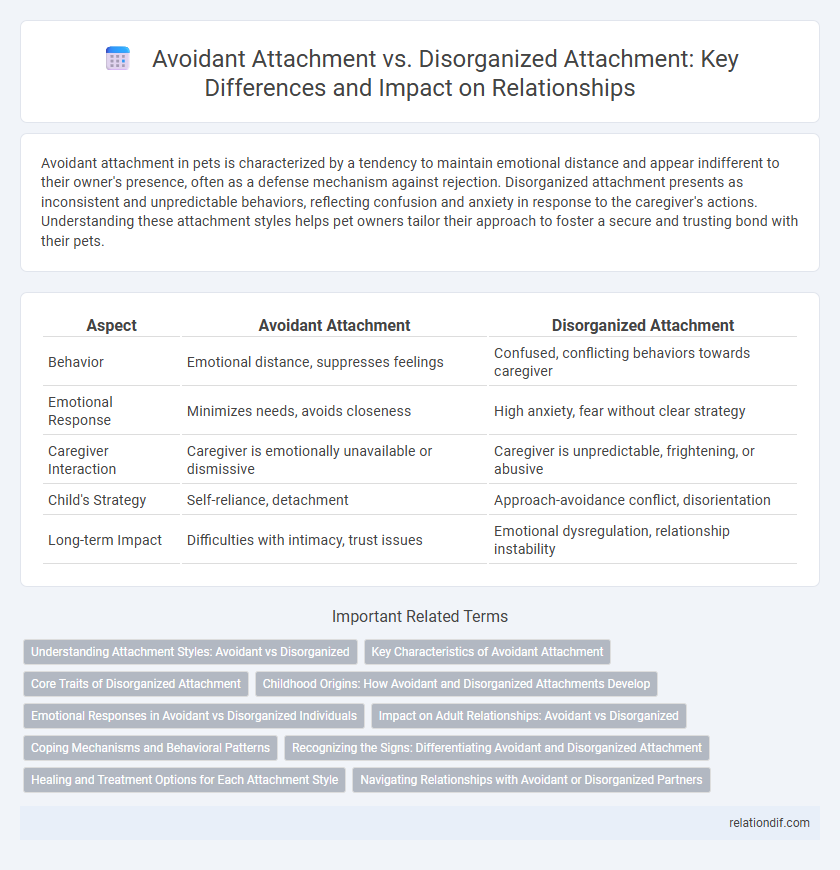
| Aspect | Avoidant Attachment | Disorganized Attachment |
|---|---|---|
| Behavior | Emotional distance, suppresses feelings | Confused, conflicting behaviors towards caregiver |
| Emotional Response | Minimizes needs, avoids closeness | High anxiety, fear without clear strategy |
| Caregiver Interaction | Caregiver is emotionally unavailable or dismissive | Caregiver is unpredictable, frightening, or abusive |
| Child's Strategy | Self-reliance, detachment | Approach-avoidance conflict, disorientation |
| Long-term Impact | Difficulties with intimacy, trust issues | Emotional dysregulation, relationship instability |
Understanding Attachment Styles: Avoidant vs Disorganized
Avoidant attachment is characterized by emotional distance and a preference for self-reliance, often stemming from caregivers' consistent unavailability or rejection. Disorganized attachment involves a chaotic mix of approach and avoidance behaviors, typically resulting from frightening or inconsistent caregiving in early childhood. Understanding these attachment styles aids in recognizing patterns of intimacy, trust, and emotional regulation in adult relationships.
Key Characteristics of Avoidant Attachment
Avoidant attachment is characterized by emotional distancing, discomfort with closeness, and a tendency to suppress feelings to maintain independence. Individuals with avoidant attachment often exhibit self-reliance, difficulty trusting others, and reluctance to seek support during stress. This attachment style contrasts with disorganized attachment, which involves mixed, unpredictable behaviors and heightened fear of abandonment.
Core Traits of Disorganized Attachment
Disorganized attachment is characterized by inconsistent and unpredictable behaviors, combining both avoidant and anxious responses toward caregivers. Core traits include fear without solution, contradictory approach-avoidance actions, and difficulty regulating emotions due to unresolved trauma or loss. This attachment style often results in confusion and mistrust in relationships, impacting emotional stability and social functioning.
Childhood Origins: How Avoidant and Disorganized Attachments Develop
Avoidant attachment develops in childhood when caregivers consistently reject or dismiss a child's emotional needs, leading the child to minimize expressions of distress and seek independence to protect themselves from further rejection. Disorganized attachment arises from inconsistent, frightening, or abusive caregiving, creating a child's confusion and fear without a clear strategy for seeking comfort. Both attachment styles stem from early interactions that disrupt secure bonding, influencing emotional regulation and relationship patterns later in life.
Emotional Responses in Avoidant vs Disorganized Individuals
Avoidant attachment is characterized by emotional suppression and discomfort with closeness, leading individuals to minimize expressions of distress and maintain emotional distance. Disorganized attachment presents with contradictory and intense emotional responses, including fear, confusion, and difficulty regulating emotions due to unresolved trauma or inconsistent caregiving. These patterns significantly impact interpersonal relationships, where avoidant individuals tend to withdraw emotionally, and disorganized individuals exhibit unpredictable emotional behavior.
Impact on Adult Relationships: Avoidant vs Disorganized
Avoidant attachment in adults often leads to emotional distance and difficulty trusting partners, resulting in challenges with intimacy and commitment. Disorganized attachment typically causes unpredictable relationship behaviors, blending fear of rejection with a strong desire for closeness, which creates instability and confusion. These distinct attachment patterns profoundly affect emotional regulation and relationship satisfaction in adult romantic connections.
Coping Mechanisms and Behavioral Patterns
Avoidant attachment manifests through self-reliance and emotional distancing as primary coping mechanisms, often leading to suppressed feelings and difficulty forming close relationships. Disorganized attachment displays inconsistent behaviors, combining approach and avoidance, driven by fear and confusion due to unresolved trauma. These patterns impact emotional regulation, with avoidant individuals minimizing distress and disorganized individuals exhibiting erratic responses to stress.
Recognizing the Signs: Differentiating Avoidant and Disorganized Attachment
Avoidant attachment is characterized by emotional distance, reluctance to seek comfort, and a consistent preference for independence, while disorganized attachment exhibits contradictory behaviors such as fearfulness, confusion, and both seeking and avoiding closeness. Recognizing the signs involves observing patterns in relationships: avoidant individuals suppress their attachment needs, whereas those with disorganized attachment display erratic responses to intimacy and stress. Identifying these distinct behavioral markers is crucial for targeted therapeutic interventions and fostering healthier relational dynamics.
Healing and Treatment Options for Each Attachment Style
Avoidant attachment typically benefits from therapies that emphasize building trust and emotional awareness, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy and mindfulness practices, which encourage safe vulnerability in relationships. Disorganized attachment requires trauma-informed approaches like Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) and Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT), focusing on integrating fragmented emotions and fostering stable emotional regulation. Both attachment styles improve through consistent, supportive therapeutic relationships that reinforce secure attachment patterns and resilience.
Navigating Relationships with Avoidant or Disorganized Partners
Navigating relationships with avoidant or disorganized partners requires understanding their core attachment styles: avoidant individuals often prioritize independence and may withdraw emotionally, while disorganized partners display conflicting behaviors due to unresolved trauma. Recognizing these patterns helps in establishing clear communication boundaries, fostering emotional safety, and promoting gradual trust-building. Consistent patience and empathy are essential for maintaining connection despite the inherent relational challenges.
Avoidant attachment vs disorganized attachment Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com