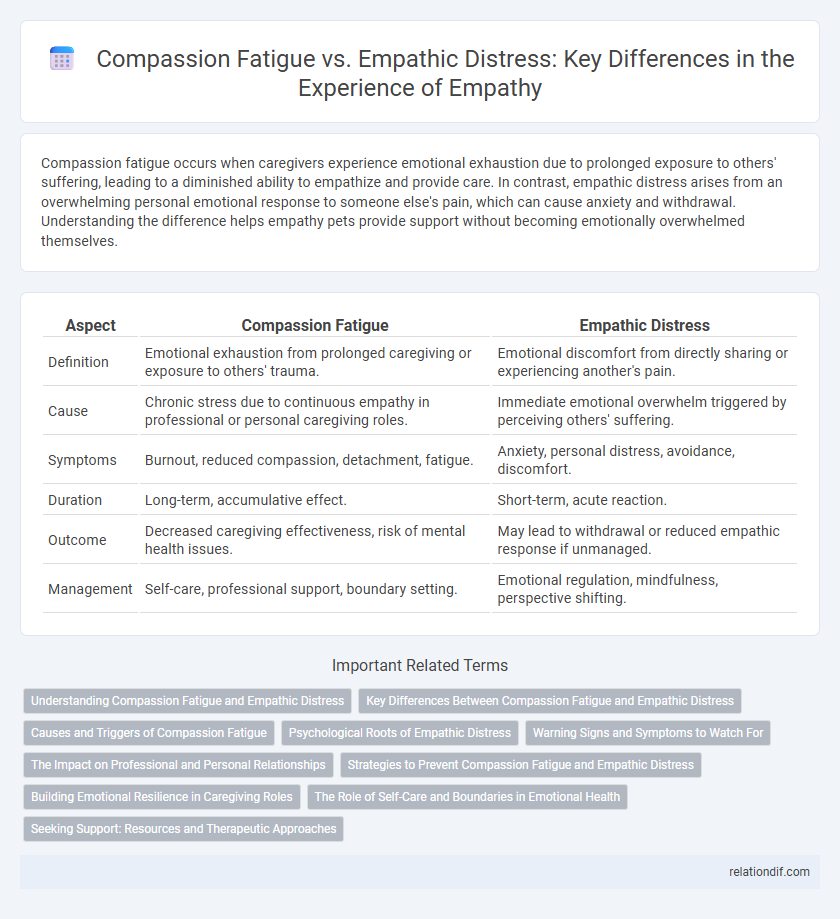
Compassion fatigue occurs when caregivers experience emotional exhaustion due to prolonged exposure to others' suffering, leading to a diminished ability to empathize and provide care. In contrast, empathic distress arises from an overwhelming personal emotional response to someone else's pain, which can cause anxiety and withdrawal. Understanding the difference helps empathy pets provide support without becoming emotionally overwhelmed themselves.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Compassion Fatigue | Empathic Distress |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Emotional exhaustion from prolonged caregiving or exposure to others' trauma. | Emotional discomfort from directly sharing or experiencing another's pain. |
| Cause | Chronic stress due to continuous empathy in professional or personal caregiving roles. | Immediate emotional overwhelm triggered by perceiving others' suffering. |
| Symptoms | Burnout, reduced compassion, detachment, fatigue. | Anxiety, personal distress, avoidance, discomfort. |
| Duration | Long-term, accumulative effect. | Short-term, acute reaction. |
| Outcome | Decreased caregiving effectiveness, risk of mental health issues. | May lead to withdrawal or reduced empathic response if unmanaged. |
| Management | Self-care, professional support, boundary setting. | Emotional regulation, mindfulness, perspective shifting. |
Understanding Compassion Fatigue and Empathic Distress
Compassion fatigue manifests as emotional exhaustion from prolonged exposure to others' suffering, impairing caregivers' ability to provide effective support. Empathic distress arises when an individual becomes overwhelmed by another's pain, triggering self-focused anxiety rather than compassionate action. Differentiating these responses is essential for implementing strategies that restore resilience and maintain empathetic engagement without burnout.
Key Differences Between Compassion Fatigue and Empathic Distress
Compassion fatigue is a state of physical and emotional exhaustion caused by prolonged exposure to others' suffering, leading to reduced empathy and burnout, whereas empathic distress is an immediate, intense emotional response to witnessing another's pain, often resulting in personal discomfort without long-term exhaustion. Key differences include compassion fatigue's association with cumulative stress and burnout, while empathic distress involves acute emotional overwhelm. Understanding these distinctions is critical for developing effective coping strategies and maintaining emotional resilience in caregiving professions.
Causes and Triggers of Compassion Fatigue
Compassion fatigue arises primarily from prolonged exposure to others' suffering, frequently triggered by continuous caregiving roles, high emotional demands, and insufficient recovery time. Key causes include secondary traumatic stress, emotional exhaustion, and the cumulative impact of bearing others' pain without adequate support. Unlike empathic distress, which is an immediate emotional response, compassion fatigue develops over time due to chronic stress and lack of self-care mechanisms.
Psychological Roots of Empathic Distress
Empathic distress originates from an overwhelming activation of brain regions responsible for emotion regulation and self-other differentiation, often linked to heightened activity in the anterior insula and the anterior cingulate cortex. Unlike compassion fatigue, which develops from chronic exposure to others' suffering and leads to emotional exhaustion, empathic distress stems from immediate, intense emotional resonance causing personal discomfort and withdrawal instincts. Understanding the psychological roots highlights the importance of self-awareness and emotional boundaries to prevent empathic distress from impairing mental health.
Warning Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
Compassion fatigue often manifests through chronic exhaustion, reduced empathy, and feelings of helplessness, signaling that caregivers may be overwhelmed by ongoing emotional demands. Empathic distress typically presents with intense emotional overwhelm, anxiety, and withdrawal as individuals absorb others' suffering without effective coping mechanisms. Recognizing these warning signs--such as irritability, sleep disturbances, and emotional numbness--is crucial for early intervention and maintaining emotional resilience.
The Impact on Professional and Personal Relationships
Compassion Fatigue and Empathic Distress both negatively affect professional and personal relationships by reducing emotional availability and increasing irritability. Compassion Fatigue often leads to burnout in caregiving professions, impairing communication and trust with colleagues and loved ones. Empathic Distress, characterized by overwhelming emotional responses, can cause withdrawal or avoidance behaviors that strain relational bonds and hinder effective support.
Strategies to Prevent Compassion Fatigue and Empathic Distress
Effective strategies to prevent compassion fatigue and empathic distress include setting emotional boundaries, practicing regular self-care, and engaging in mindfulness techniques to maintain mental resilience. Seeking support through counseling or peer support groups helps process emotional experiences and reduce the risk of burnout. Prioritizing work-life balance and continuous professional development enhances coping skills and sustains empathy in high-stress caregiving environments.
Building Emotional Resilience in Caregiving Roles
Compassion fatigue and empathic distress are critical challenges faced by caregivers, often leading to emotional exhaustion and diminished caregiving effectiveness. Building emotional resilience involves implementing strategies such as mindfulness, boundary-setting, and self-care routines to mitigate the impact of prolonged exposure to others' suffering. Developing resilience enhances caregivers' capacity to maintain empathy while protecting their mental health, ensuring sustained compassion and professional performance.
The Role of Self-Care and Boundaries in Emotional Health
Compassion fatigue arises from prolonged exposure to others' suffering, leading to emotional exhaustion and diminished capacity to empathize, while empathic distress results from overwhelming personal emotional response to others' pain. Effective self-care practices, such as mindfulness, regular physical activity, and adequate rest, help replenish emotional resources and prevent burnout. Establishing clear boundaries protects emotional health by allowing caregivers to manage their empathy without becoming overwhelmed.
Seeking Support: Resources and Therapeutic Approaches
Seeking support is essential in managing compassion fatigue and empathic distress, with therapeutic approaches like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) showing significant efficacy. Accessing resources such as peer support groups, professional counseling, and resilience training programs helps individuals develop coping strategies and emotional regulation skills. Early intervention through these targeted supports reduces burnout and promotes psychological well-being among caregivers and empathic individuals.
Compassion Fatigue vs Empathic Distress Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com