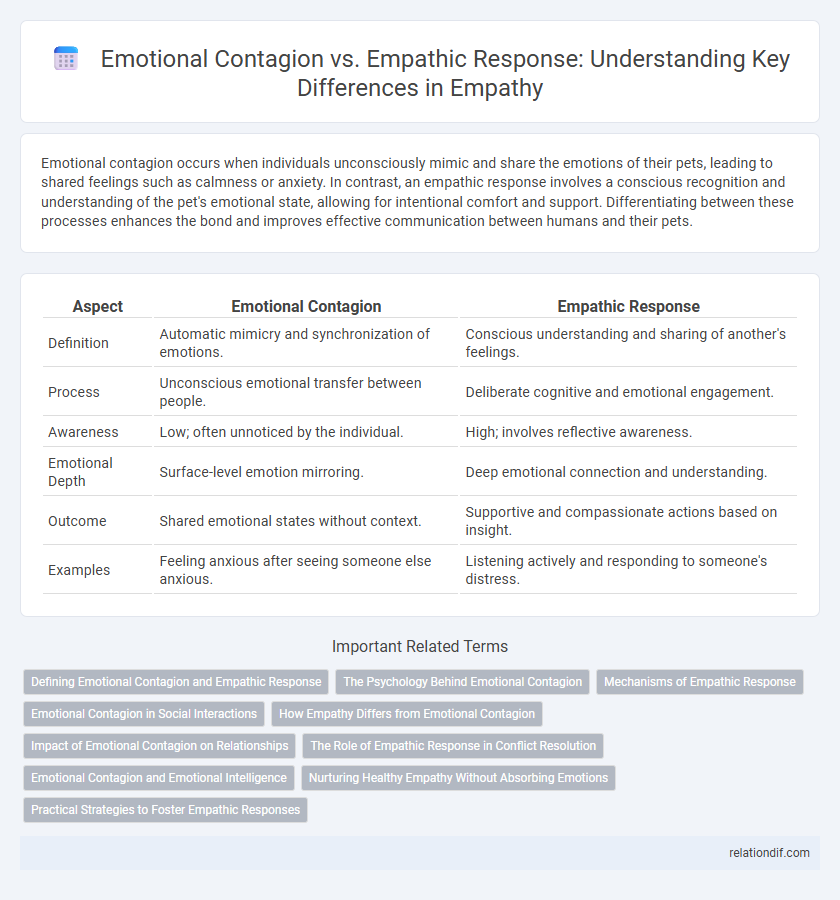
Emotional contagion occurs when individuals unconsciously mimic and share the emotions of their pets, leading to shared feelings such as calmness or anxiety. In contrast, an empathic response involves a conscious recognition and understanding of the pet's emotional state, allowing for intentional comfort and support. Differentiating between these processes enhances the bond and improves effective communication between humans and their pets.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Emotional Contagion | Empathic Response |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automatic mimicry and synchronization of emotions. | Conscious understanding and sharing of another's feelings. |
| Process | Unconscious emotional transfer between people. | Deliberate cognitive and emotional engagement. |
| Awareness | Low; often unnoticed by the individual. | High; involves reflective awareness. |
| Emotional Depth | Surface-level emotion mirroring. | Deep emotional connection and understanding. |
| Outcome | Shared emotional states without context. | Supportive and compassionate actions based on insight. |
| Examples | Feeling anxious after seeing someone else anxious. | Listening actively and responding to someone's distress. |
Defining Emotional Contagion and Empathic Response
Emotional contagion refers to the automatic synchronization of emotions between individuals, where one person unconsciously "catches" the feelings of another, often through nonverbal cues like facial expressions and tone of voice. In contrast, empathic response involves a conscious cognitive process where one recognizes, understands, and responds to another's emotional state with appropriate concern or support. While emotional contagion is an involuntary experience, empathic response requires deliberate mental engagement and perspective-taking.
The Psychology Behind Emotional Contagion
Emotional contagion involves the automatic, subconscious transfer of emotions from one person to another through nonverbal cues like facial expressions and body language, activating mirror neuron systems in the brain. This phenomenon differs from empathic response, which requires conscious awareness and cognitive processing to understand and share another's emotional state. Psychological studies reveal that emotional contagion relies on implicit neural mechanisms that facilitate social bonding, while empathic response engages higher-order brain regions such as the anterior insula and medial prefrontal cortex for perspective-taking and emotional regulation.
Mechanisms of Empathic Response
Empathic response involves complex neural mechanisms, including mirror neuron activation and the engagement of the anterior insula and anterior cingulate cortex, which facilitate the understanding and sharing of another's emotional state. Unlike emotional contagion, which is an automatic, subconscious mimicry leading to shared emotions, empathic response requires cognitive appraisal and perspective-taking to differentiate self from other. This process enables regulated emotional reactions and supportive behavioral intentions, crucial in social bonding and prosocial behavior.
Emotional Contagion in Social Interactions
Emotional contagion in social interactions occurs when individuals unconsciously mimic and synchronize emotions with others, leading to a shared emotional experience that enhances group cohesion. This phenomenon plays a critical role in nonverbal communication, where facial expressions, vocal tones, and body language trigger automatic affective responses. Understanding emotional contagion helps explain collective moods in teams, crowds, and social networks, influencing decision-making and interpersonal dynamics.
How Empathy Differs from Emotional Contagion
Empathy involves understanding and sharing another person's feelings with conscious awareness, while emotional contagion is the automatic, unconscious mimicry of emotions experienced by others. Unlike emotional contagion, which occurs without deliberate cognitive processing, empathy requires active perspective-taking and emotional regulation to respond appropriately. The distinction lies in empathy's combination of affective resonance and cognitive evaluation, enabling more nuanced social interactions and emotional support.
Impact of Emotional Contagion on Relationships
Emotional contagion significantly influences relationships by transmitting feelings rapidly between individuals, often intensifying shared emotional experiences and fostering deeper social bonds. This automatic process can amplify both positive and negative emotions, shaping the overall emotional climate and affecting communication patterns within relationships. Understanding emotional contagion helps in managing interpersonal dynamics and enhancing empathic responses for healthier and more supportive connections.
The Role of Empathic Response in Conflict Resolution
Empathic response plays a crucial role in conflict resolution by fostering active listening and genuine understanding of opposing perspectives. Unlike emotional contagion, which merely involves mirroring emotions, empathic response enables individuals to process and address underlying needs and concerns constructively. This deeper emotional engagement facilitates trust-building and collaborative problem-solving, essential for lasting conflict resolution.
Emotional Contagion and Emotional Intelligence
Emotional contagion refers to the automatic and unconscious transfer of emotions from one person to another, significantly influenced by nonverbal cues and facial expressions. High emotional intelligence enhances the ability to recognize and manage these transmitted emotions, allowing individuals to respond thoughtfully rather than react impulsively. Understanding emotional contagion aids in improving social interactions and fostering empathetic connections in both personal and professional environments.
Nurturing Healthy Empathy Without Absorbing Emotions
Emotional contagion involves automatically absorbing others' feelings, which can lead to emotional overwhelm and burnout. An empathic response requires conscious awareness and regulation, allowing individuals to understand and support others without internalizing their emotions. Developing boundaries and practicing self-care are essential strategies for nurturing healthy empathy while preventing emotional exhaustion.
Practical Strategies to Foster Empathic Responses
Cultivating empathic responses involves active listening to understand others' emotions rather than merely mirroring feelings, which characterizes emotional contagion. Techniques such as reflective questioning and perspective-taking help individuals engage thoughtfully with others' experiences, promoting deeper emotional insight. Training programs incorporating mindfulness and emotional regulation skills enhance the ability to respond empathetically, fostering more meaningful interpersonal connections.
Emotional Contagion vs Empathic Response Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com