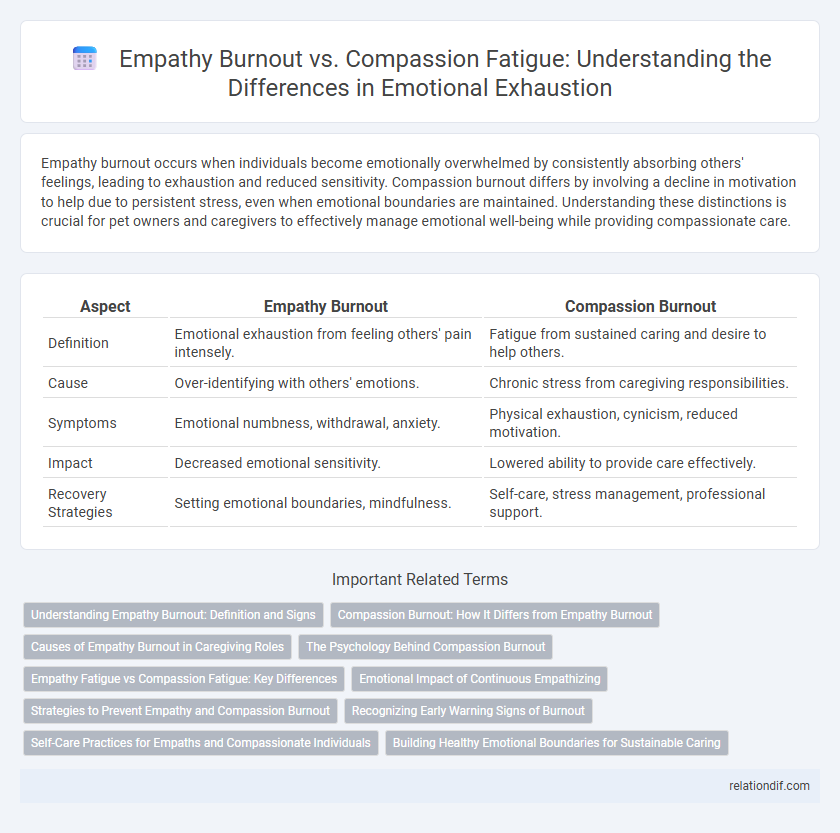
Empathy burnout occurs when individuals become emotionally overwhelmed by consistently absorbing others' feelings, leading to exhaustion and reduced sensitivity. Compassion burnout differs by involving a decline in motivation to help due to persistent stress, even when emotional boundaries are maintained. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for pet owners and caregivers to effectively manage emotional well-being while providing compassionate care.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Empathy Burnout | Compassion Burnout |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Emotional exhaustion from feeling others' pain intensely. | Fatigue from sustained caring and desire to help others. |
| Cause | Over-identifying with others' emotions. | Chronic stress from caregiving responsibilities. |
| Symptoms | Emotional numbness, withdrawal, anxiety. | Physical exhaustion, cynicism, reduced motivation. |
| Impact | Decreased emotional sensitivity. | Lowered ability to provide care effectively. |
| Recovery Strategies | Setting emotional boundaries, mindfulness. | Self-care, stress management, professional support. |
Understanding Empathy Burnout: Definition and Signs
Empathy burnout occurs when prolonged exposure to others' emotional distress overwhelms an individual's capacity to emotionally connect, leading to exhaustion and detachment. Key signs include persistent fatigue, reduced ability to feel compassion, irritability, and decreased productivity. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for preventing long-term emotional and psychological consequences associated with empathy fatigue.
Compassion Burnout: How It Differs from Empathy Burnout
Compassion burnout occurs when individuals become emotionally drained from prolonged exposure to others' suffering, leading to reduced capacity to care. Unlike empathy burnout, which stems from absorbing others' emotions deeply, compassion burnout results from the overwhelming pressure of continuous caregiving responsibilities. Recognizing these differences helps implement targeted self-care strategies to prevent exhaustion in caregiving professions.
Causes of Empathy Burnout in Caregiving Roles
Empathy burnout in caregiving roles primarily arises from chronic emotional exhaustion due to continuous exposure to others' pain and suffering, which overwhelms the caregiver's emotional resources. High interpersonal demands, lack of adequate support systems, and insufficient recovery time exacerbate this condition, leading to reduced empathy capacity and emotional numbness. Unlike compassion burnout, empathy burnout is characterized by an intense personal emotional resonance with the distress experienced by care recipients, resulting in mental fatigue and decreased caregiving effectiveness.
The Psychology Behind Compassion Burnout
Compassion burnout arises from prolonged emotional exposure to others' suffering, leading to emotional exhaustion and reduced capacity for empathy. Psychological mechanisms involve chronic stress responses that diminish the brain's ability to regulate emotions effectively, impairing professional caregivers' resilience. Understanding the neurobiological impact of compassion fatigue highlights the importance of self-care and therapeutic interventions in preventing empathy erosion and maintaining emotional well-being.
Empathy Fatigue vs Compassion Fatigue: Key Differences
Empathy fatigue occurs when individuals become emotionally overwhelmed by continually absorbing others' distress, leading to emotional exhaustion and reduced ability to connect. Compassion fatigue, on the other hand, arises from the strain of caregiving roles and results in diminished empathy and increased feelings of helplessness or cynicism. Understanding the key differences between empathy fatigue and compassion fatigue is crucial for developing targeted strategies to manage emotional well-being in professionals exposed to chronic stress.
Emotional Impact of Continuous Empathizing
Continuous empathizing often leads to empathy burnout, characterized by emotional exhaustion and decreased ability to connect with others' feelings. Unlike compassion burnout, which stems from prolonged exposure to others' suffering and a sense of helplessness, empathy burnout primarily involves overwhelming emotional contagion and personal distress. Recognizing these differences is crucial for implementing effective self-care strategies to maintain emotional resilience and professional effectiveness.
Strategies to Prevent Empathy and Compassion Burnout
Effective strategies to prevent empathy and compassion burnout include establishing clear emotional boundaries and practicing regular self-care routines such as mindfulness and stress management techniques. Engaging in peer support groups and seeking professional supervision helps maintain emotional resilience and promotes healthy detachment from clients' trauma. Incorporating restorative practices like adequate rest, physical exercise, and hobbies enhances overall well-being and reduces the risk of emotional exhaustion.
Recognizing Early Warning Signs of Burnout
Recognizing early warning signs of empathy burnout includes emotional exhaustion, decreased ability to connect with others, and feelings of detachment or cynicism. Compassion burnout often presents through chronic fatigue, irritability, and reduced personal accomplishment despite continued caregiving efforts. Identifying these symptoms promptly allows for proactive self-care and professional support to prevent long-term psychological distress.
Self-Care Practices for Empaths and Compassionate Individuals
Empathy burnout arises from emotional overextension in deeply feeling others' pain, whereas compassion burnout stems from prolonged exposure to suffering combined with a perceived inability to alleviate it. Effective self-care practices for empaths and compassionate individuals include regular emotional boundary-setting, mindfulness meditation, and engaging in restorative activities such as nature walks or creative arts. Prioritizing adequate sleep, balanced nutrition, and professional support can further sustain emotional resilience and prevent burnout.
Building Healthy Emotional Boundaries for Sustainable Caring
Empathy burnout occurs when individuals over-identify with others' emotions, leading to emotional exhaustion, while compassion burnout results from prolonged exposure to others' suffering without adequate self-care. Building healthy emotional boundaries involves recognizing personal limits, practicing self-compassion, and maintaining a balanced emotional engagement to prevent overwhelm and sustain caregiving capacity. Strategies such as mindfulness, regular emotional check-ins, and seeking support enhance resilience, fostering sustainable caring without sacrificing well-being.
Empathy burnout vs compassion burnout Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com