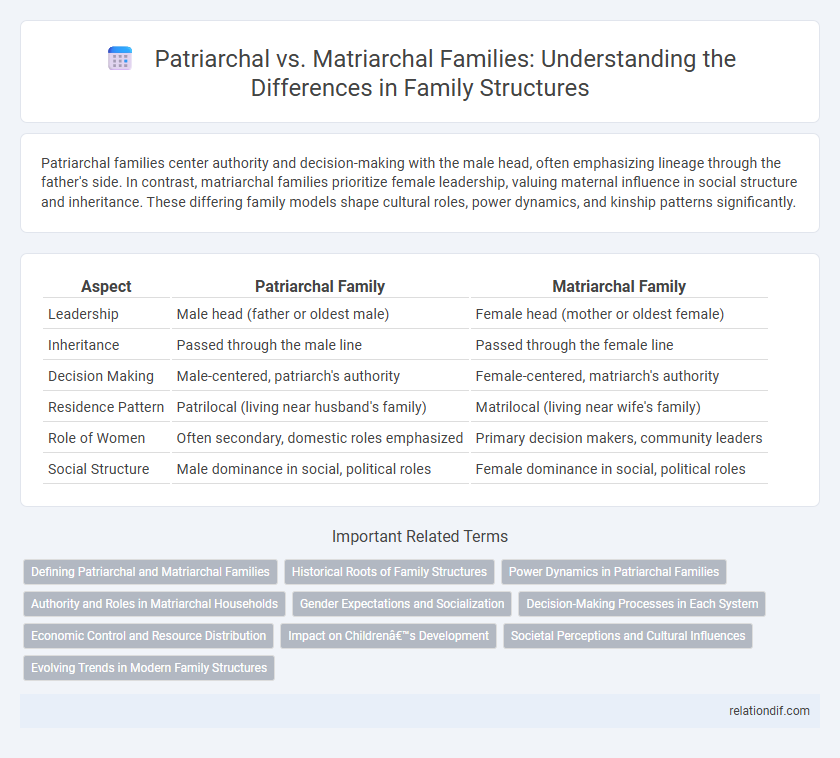
Patriarchal families center authority and decision-making with the male head, often emphasizing lineage through the father's side. In contrast, matriarchal families prioritize female leadership, valuing maternal influence in social structure and inheritance. These differing family models shape cultural roles, power dynamics, and kinship patterns significantly.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Patriarchal Family | Matriarchal Family |
|---|---|---|
| Leadership | Male head (father or oldest male) | Female head (mother or oldest female) |
| Inheritance | Passed through the male line | Passed through the female line |
| Decision Making | Male-centered, patriarch's authority | Female-centered, matriarch's authority |
| Residence Pattern | Patrilocal (living near husband's family) | Matrilocal (living near wife's family) |
| Role of Women | Often secondary, domestic roles emphasized | Primary decision makers, community leaders |
| Social Structure | Male dominance in social, political roles | Female dominance in social, political roles |
Defining Patriarchal and Matriarchal Families
Patriarchal families are structured with the father or eldest male acting as the head of the household, holding primary authority over family decisions, inheritance, and social roles. Matriarchal families, in contrast, revolve around the mother or eldest female who leads familial governance, social organization, and inheritance patterns. These opposing family systems influence power dynamics, gender roles, and lineage tracing within societies.
Historical Roots of Family Structures
Patriarchal family structures have roots in ancient agricultural societies where male dominance was reinforced by land ownership and inheritance laws. Matriarchal families, observed in various Indigenous cultures, emphasize female authority linked to clan lineage and resource distribution. Historical shifts in economy, religion, and social organization shaped the prominence of these family models across civilizations.
Power Dynamics in Patriarchal Families
Power dynamics in patriarchal families center around male authority, where fathers or male elders hold primary control over decision-making, property ownership, and familial roles. Women and children typically assume subordinate positions, with limited influence over financial resources and social status. This hierarchical structure shapes interpersonal relationships and enforces gender norms within the household.
Authority and Roles in Matriarchal Households
Matriarchal households center authority around the eldest woman, often a grandmother or mother, who holds decision-making power and oversees family welfare. Roles in these families emphasize cooperative child-rearing, with women managing domestic responsibilities and inheritance typically passing through the maternal line. This structure fosters strong female leadership and communal support, contrasting with patriarchal emphasis on male dominance and lineage.
Gender Expectations and Socialization
Patriarchal families typically emphasize traditional gender roles, where men are expected to be the primary authority figures and breadwinners, while women often take on caregiving and domestic responsibilities. In contrast, matriarchal families may promote female leadership and decision-making, challenging conventional male dominance and encouraging diverse gender role socialization. These differing structures shape individual identities and societal expectations by reinforcing or redefining gender norms through family dynamics and upbringing.
Decision-Making Processes in Each System
Patriarchal families centralize decision-making power primarily with the male head of household, reflecting a hierarchy where authority is often inherited and reinforced through cultural norms. Matriarchal families distribute decision-making more communally, with female leaders or elders guiding major family choices, often prioritizing consensus and collective well-being. These distinct structures influence family dynamics, resource allocation, and conflict resolution, shaping the social roles within each system.
Economic Control and Resource Distribution
In patriarchal families, economic control typically resides with male heads who dominate decision-making and resource allocation, reflecting traditional gender roles that prioritize male authority. Matriarchal families often see women managing household finances and distributing resources, promoting equitable access within the family unit and empowering female economic leadership. These differing structures impact financial priorities, inheritance practices, and investment in family welfare, shaping the overall economic dynamics of the household.
Impact on Children’s Development
Patriarchal families often emphasize hierarchical roles, where fathers typically hold authority, influencing children's development through discipline and traditional gender role modeling. In contrast, matriarchal families tend to foster nurturing and communicative environments led by mothers, promoting emotional intelligence and collaborative skills in children. Research indicates that children in both family structures benefit from strong parental involvement but develop differently based on role distribution and emotional support patterns.
Societal Perceptions and Cultural Influences
Societal perceptions of patriarchal families often emphasize male authority and traditional gender roles, reinforcing cultural norms that prioritize paternal leadership and lineage. In contrast, matriarchal families are viewed through the lens of female-centered authority, often challenging conventional hierarchies and promoting communal decision-making. Cultural influences shape these family structures by legitimizing power dynamics and social expectations, impacting inheritance, caregiving roles, and social status within communities.
Evolving Trends in Modern Family Structures
Patriarchal families traditionally centralize authority with the male head, emphasizing lineage and inheritance through male descendants, while matriarchal families prioritize female leadership and maternal influence. Modern family structures increasingly blend these models, reflecting shifts toward gender equality, shared responsibilities, and diverse caregiving roles across cultures. Statistical studies reveal a rise in dual-income households and egalitarian decision-making patterns, underscoring evolving trends in family dynamics worldwide.
patriarchal family vs matriarchal family Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com