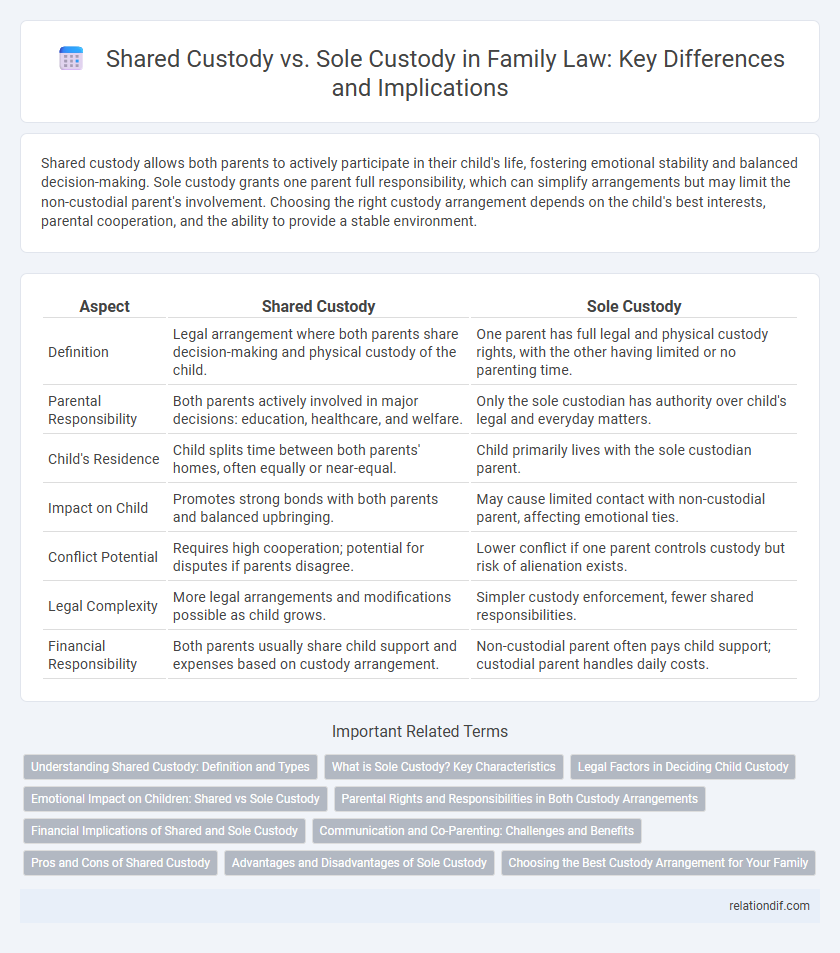
Shared custody allows both parents to actively participate in their child's life, fostering emotional stability and balanced decision-making. Sole custody grants one parent full responsibility, which can simplify arrangements but may limit the non-custodial parent's involvement. Choosing the right custody arrangement depends on the child's best interests, parental cooperation, and the ability to provide a stable environment.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Shared Custody | Sole Custody |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal arrangement where both parents share decision-making and physical custody of the child. | One parent has full legal and physical custody rights, with the other having limited or no parenting time. |
| Parental Responsibility | Both parents actively involved in major decisions: education, healthcare, and welfare. | Only the sole custodian has authority over child's legal and everyday matters. |
| Child's Residence | Child splits time between both parents' homes, often equally or near-equal. | Child primarily lives with the sole custodian parent. |
| Impact on Child | Promotes strong bonds with both parents and balanced upbringing. | May cause limited contact with non-custodial parent, affecting emotional ties. |
| Conflict Potential | Requires high cooperation; potential for disputes if parents disagree. | Lower conflict if one parent controls custody but risk of alienation exists. |
| Legal Complexity | More legal arrangements and modifications possible as child grows. | Simpler custody enforcement, fewer shared responsibilities. |
| Financial Responsibility | Both parents usually share child support and expenses based on custody arrangement. | Non-custodial parent often pays child support; custodial parent handles daily costs. |
Understanding Shared Custody: Definition and Types
Shared custody involves both parents having legal and physical responsibility for their child, allowing joint decision-making and time allocation. Types include joint legal custody, where parents share the authority to make important decisions, and joint physical custody, where the child spends significant time living with each parent. This arrangement promotes balanced parental involvement, fostering stability and emotional support for the child.
What is Sole Custody? Key Characteristics
Sole custody grants one parent the exclusive legal and physical responsibility for a child's care, decision-making, and residence. This parent has the authority to make major life decisions regarding education, healthcare, and religious upbringing without requiring consent from the other parent. Key characteristics include the child's primary living arrangement with the custodial parent and limited visitation rights granted to the non-custodial parent.
Legal Factors in Deciding Child Custody
Legal factors in deciding child custody center on the child's best interests, evaluating each parent's ability to provide a stable, safe environment and meet the child's emotional and physical needs. Courts consider parental history, including any evidence of abuse or neglect, as well as each parent's willingness to foster a positive relationship with the other parent. Shared custody is often favored when both parents demonstrate cooperative co-parenting capabilities, whereas sole custody is awarded when one parent's involvement is deemed detrimental or impractical.
Emotional Impact on Children: Shared vs Sole Custody
Shared custody often leads to more stable emotional development in children by maintaining strong relationships with both parents, reducing feelings of abandonment and insecurity. Sole custody can increase the risk of emotional stress and anxiety due to limited contact with the non-custodial parent, potentially causing feelings of loss or divided loyalty. Research indicates children in shared custody arrangements generally exhibit better psychological well-being and social adjustment compared to those in sole custody settings.
Parental Rights and Responsibilities in Both Custody Arrangements
Shared custody grants both parents equal rights and responsibilities in decision-making, child-rearing, and day-to-day care, promoting active involvement and cooperation. Sole custody assigns primary decision-making authority and physical custody to one parent, while the non-custodial parent typically retains visitation rights and some parental responsibilities. Legal frameworks ensure both custody types prioritize the child's best interests, balancing parental rights with responsibilities such as education, healthcare, and emotional support.
Financial Implications of Shared and Sole Custody
Shared custody often results in more balanced financial responsibilities, with both parents contributing to child-related expenses such as education, healthcare, and daily needs, potentially reducing the financial burden on a single parent. Sole custody typically places the majority of financial obligations on the custodial parent, who may receive child support payments to offset costs but often bears higher expenses overall. Understanding legal guidelines and state-specific child support calculations is crucial for accurately assessing the economic impact of custody arrangements.
Communication and Co-Parenting: Challenges and Benefits
Effective communication is essential in shared custody arrangements, enabling both parents to coordinate schedules and ensure consistent child-rearing practices, which benefits the child's stability and emotional well-being. Sole custody may reduce interparental communication challenges but can place the full responsibility of decision-making on one parent, potentially limiting the child's exposure to diverse parental perspectives. Overcoming communication barriers in shared custody fosters collaborative co-parenting, promoting mutual respect and a supportive environment for the child's development.
Pros and Cons of Shared Custody
Shared custody promotes balanced parental involvement, fostering emotional stability and stronger child-parent relationships by allowing children to maintain meaningful contact with both parents consistently. It can reduce feelings of abandonment and improve co-parenting communication, yet logistical challenges such as coordinating schedules and potential conflicts may arise, impacting the child's routine. Courts often favor shared custody when parents demonstrate cooperation and prioritize the child's best interests, but in cases of high conflict, it may increase stress and undermine the child's well-being.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Sole Custody
Sole custody grants one parent full legal and physical responsibility for a child, offering clear decision-making authority and stability in the child's living arrangements. This arrangement can reduce conflicts between parents and provide consistency, but it may limit the non-custodial parent's involvement and affect the child's relationship with that parent. Potential drawbacks include increased emotional and financial burden on the custodial parent and possible feelings of alienation in the child.
Choosing the Best Custody Arrangement for Your Family
Choosing the best custody arrangement for your family depends on the child's emotional well-being and stability. Shared custody allows both parents to remain actively involved in the child's life, promoting balanced relationships and consistent support. Sole custody may be necessary in situations involving safety concerns or parental conflict, ensuring the child's needs come first.
shared custody vs sole custody Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com