Consummation is the physical act that completes a marriage, establishing its legal and emotional validity. Annulment, however, declares a marriage null and void as if it never existed, often due to factors like lack of consummation, fraud, or incapacity. The key distinction lies in consummation affirming the union's legitimacy, while annulment dissolves it retroactively.
Table of Comparison
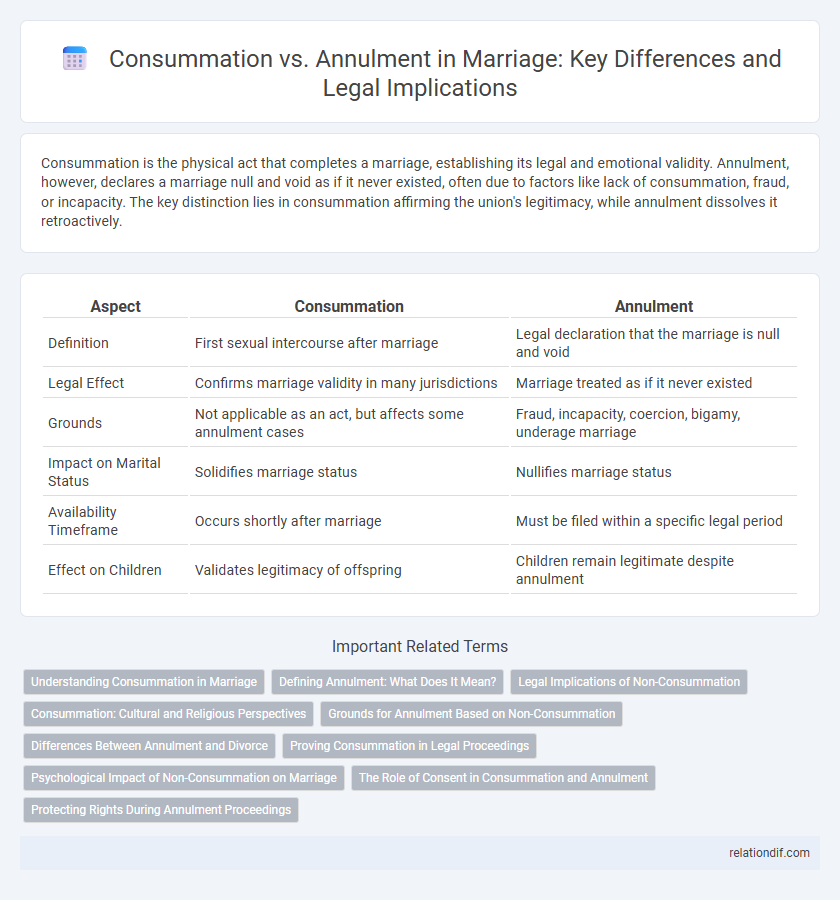
| Aspect | Consummation | Annulment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | First sexual intercourse after marriage | Legal declaration that the marriage is null and void |
| Legal Effect | Confirms marriage validity in many jurisdictions | Marriage treated as if it never existed |
| Grounds | Not applicable as an act, but affects some annulment cases | Fraud, incapacity, coercion, bigamy, underage marriage |
| Impact on Marital Status | Solidifies marriage status | Nullifies marriage status |
| Availability Timeframe | Occurs shortly after marriage | Must be filed within a specific legal period |
| Effect on Children | Validates legitimacy of offspring | Children remain legitimate despite annulment |
Understanding Consummation in Marriage
Consummation in marriage refers to the first act of sexual intercourse between spouses, often regarded as a critical factor for the validity of the marital union in many legal systems. Failure to consummate the marriage can be grounds for annulment, as it indicates the marriage was never fully realized or validated through intimate union. Understanding consummation's role helps clarify why courts may grant annulments when the marriage is unconsummated, emphasizing its importance in both legal and cultural contexts.
Defining Annulment: What Does It Mean?
Annulment in marriage legally declares the union null and void, as if it never existed, based on specific grounds such as fraud, coercion, or incapacity. Unlike divorce, which ends a valid marriage, annulment requires proving that the marriage was invalid from the start, often before or shortly after consummation. This distinction affects legal rights, property division, and status, emphasizing the importance of understanding annulment's criteria within family law.
Legal Implications of Non-Consummation
Non-consummation of marriage carries significant legal implications, often serving as valid grounds for annulment in various jurisdictions. Courts may consider the inability or refusal to consummate a marriage as evidence that the marriage is voidable, impacting rights related to property division, spousal support, and inheritance. Legal statutes differ widely, but many recognize non-consummation as a crucial factor in dissolving a marriage without the need for proving fault or separation.
Consummation: Cultural and Religious Perspectives
Consummation holds significant cultural and religious importance as it often symbolizes the official validation of a marriage and the union's sacred nature. In many religious traditions, consummation is essential for the marriage to be recognized as complete and binding, influencing practices in Christianity, Islam, and Hinduism. The lack of consummation can be grounds for annulment in various jurisdictions, reflecting its central role in the spiritual and legal acknowledgment of marital status.
Grounds for Annulment Based on Non-Consummation
Non-consummation of marriage serves as a significant ground for annulment in many jurisdictions, as it implies the physical union essential to marriage has not occurred. Legal frameworks often require proof that consummation is impossible or refused without valid reason, directly impacting the validity of the marital contract. Courts typically evaluate evidence such as declarations from both parties and medical reports to determine non-consummation before granting an annulment.
Differences Between Annulment and Divorce
Consummation refers to the first act of sexual intercourse between spouses, which legally validates the marriage, whereas annulment declares the marriage null and void as if it never existed due to factors like fraud or incapacity. Annulment differs from divorce because it erases the marriage's legal status from the beginning, while divorce ends a valid marriage through a legal dissolution process. Courts grant annulments based on specific grounds such as lack of consent or underage marriage, contrasting with divorce, which typically involves issues like irreconcilable differences or fault.
Proving Consummation in Legal Proceedings
Proving consummation in legal proceedings often requires presenting evidence such as witness testimony, medical reports, or personal affidavits confirming the couple engaged in sexual intercourse after marriage. The absence of consummation can be grounds for annulment, making the burden of proof critical in disputes over the validity of the marriage. Courts scrutinize these proofs carefully to determine whether annulling the marriage is justified under family law statutes.
Psychological Impact of Non-Consummation on Marriage
Non-consummation of marriage can lead to significant psychological distress for both partners, often resulting in feelings of rejection, inadequacy, and emotional disconnection. This lack of physical intimacy may exacerbate underlying marital conflicts, increasing tension and reducing overall relationship satisfaction. Counseling and open communication are critical in addressing these psychological impacts and exploring potential pathways, including annulment, legal separation, or reconciliation.
The Role of Consent in Consummation and Annulment
Consent plays a pivotal role in both consummation and annulment of a marriage, as it validates the union through mutual agreement to engage in marital relations. Lack of consent to consummate the marriage can serve as legal grounds for annulment, emphasizing that the marriage was never fully established. Courts often evaluate whether consent was informed and freely given to determine the legitimacy of consummation and the possibility of annulment.
Protecting Rights During Annulment Proceedings
Consummation establishes the legal validity of a marriage, making annulment more complex as rights and obligations are fully recognized upon completion. During annulment proceedings, protecting rights entails safeguarding property distribution, spousal support, and custody arrangements, especially when consummation has occurred. Courts carefully evaluate evidence of consummation to determine the appropriate legal protections for both parties and preserve fair outcomes.
consummation vs annulment Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com