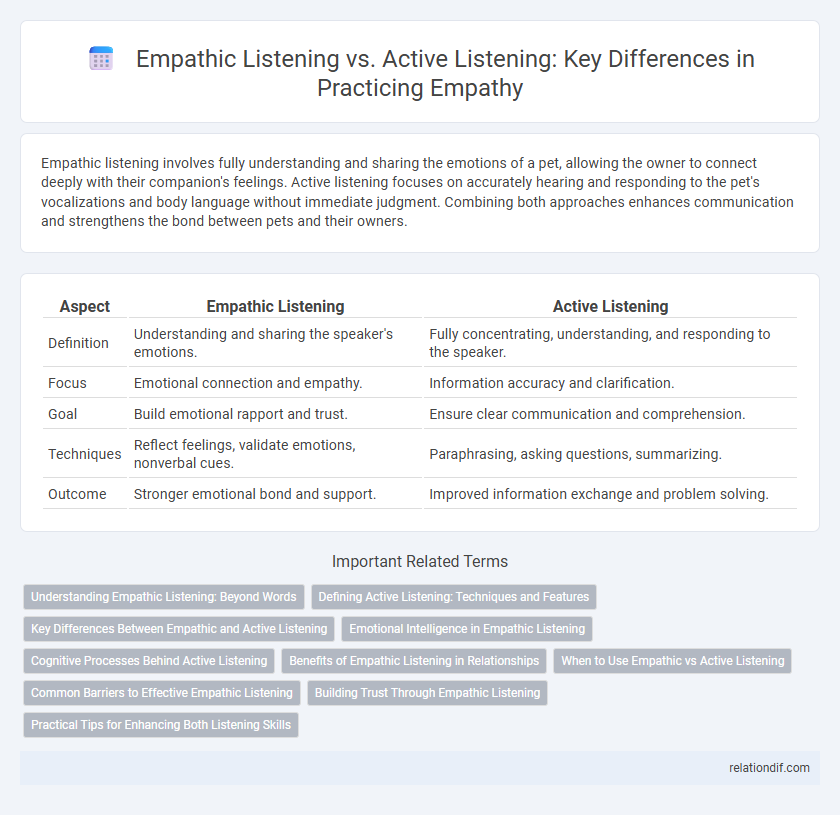
Empathic listening involves fully understanding and sharing the emotions of a pet, allowing the owner to connect deeply with their companion's feelings. Active listening focuses on accurately hearing and responding to the pet's vocalizations and body language without immediate judgment. Combining both approaches enhances communication and strengthens the bond between pets and their owners.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Empathic Listening | Active Listening |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Understanding and sharing the speaker's emotions. | Fully concentrating, understanding, and responding to the speaker. |
| Focus | Emotional connection and empathy. | Information accuracy and clarification. |
| Goal | Build emotional rapport and trust. | Ensure clear communication and comprehension. |
| Techniques | Reflect feelings, validate emotions, nonverbal cues. | Paraphrasing, asking questions, summarizing. |
| Outcome | Stronger emotional bond and support. | Improved information exchange and problem solving. |
Understanding Empathic Listening: Beyond Words
Empathic listening transcends active listening by focusing on the emotional experience behind the speaker's words, enabling deeper connection and trust. This listening approach requires tuning into nonverbal cues, such as tone, facial expressions, and body language, to fully grasp the speaker's feelings and perspectives. Empathic listening fosters emotional validation and supports healing, making it essential in counseling, conflict resolution, and personal relationships.
Defining Active Listening: Techniques and Features
Active listening involves fully concentrating, understanding, responding, and remembering what is being said. Techniques include maintaining eye contact, nodding, summarizing, and asking open-ended questions to ensure clarity and engagement. Key features emphasize non-verbal cues, paraphrasing, and providing feedback to validate the speaker's message.
Key Differences Between Empathic and Active Listening
Empathic listening centers on understanding and sharing the speaker's feelings, fostering emotional connection and validation, while active listening focuses on accurately receiving and interpreting the message through gestures like nodding and paraphrasing. Empathic listeners prioritize emotional resonance and non-judgmental presence, whereas active listeners emphasize clarity, feedback, and comprehension of the content. The key difference lies in empathic listening's goal of emotional support versus active listening's goal of information processing and response.
Emotional Intelligence in Empathic Listening
Empathic listening, a key component of emotional intelligence, involves fully understanding and resonating with the speaker's emotions, whereas active listening primarily focuses on accurately receiving and reflecting the content of the message. Emotional intelligence enhances empathic listening by enabling individuals to recognize subtle emotional cues and respond with genuine empathy, fostering deeper connection and trust. This heightened awareness supports effective communication, conflict resolution, and emotional support, making empathic listening crucial for personal and professional relationships.
Cognitive Processes Behind Active Listening
Active listening engages cognitive processes such as attention control, working memory, and information processing to accurately decode and interpret the speaker's message. Empathic listening goes beyond these functions by involving theory of mind and emotional resonance to understand the speaker's feelings and perspectives deeply. Cognitive mechanisms in active listening facilitate message retention and response formulation, while empathic listening integrates affective components to foster emotional connection and support.
Benefits of Empathic Listening in Relationships
Empathic listening strengthens relationships by fostering deeper emotional connections and understanding, which enhances trust and reduces conflicts. Unlike active listening, which centers on accurately hearing content, empathic listening focuses on grasping the speaker's feelings and perspectives, promoting validation and emotional support. This approach encourages open communication and resilience in relationships, leading to greater intimacy and mutual respect.
When to Use Empathic vs Active Listening
Empathic listening is most effective in emotionally charged situations where understanding feelings and building trust are crucial, such as in counseling or conflict resolution. Active listening suits informational or problem-solving contexts where clarity, feedback, and detailed comprehension are needed, like in professional meetings or educational settings. Choosing between empathic and active listening depends on the goal: prioritize empathy to connect on an emotional level, and active listening to ensure accuracy and mutual understanding.
Common Barriers to Effective Empathic Listening
Common barriers to effective empathic listening include distractions, prejudgments, and emotional reactivity that prevent full engagement with the speaker's feelings. Cognitive biases and a lack of genuine interest often lead listeners to respond prematurely, undermining deep understanding. Overcoming these obstacles requires conscious effort to suspend judgment and maintain focused, emotionally attuned attention throughout the conversation.
Building Trust Through Empathic Listening
Empathic listening involves deeply understanding the speaker's feelings and perspectives, which fosters genuine emotional connection and builds trust. Unlike active listening that emphasizes verbal feedback and comprehension, empathic listening prioritizes mirroring emotions and validating the speaker's experience. This approach creates a safe communication environment that enhances relational bonds and encourages openness.
Practical Tips for Enhancing Both Listening Skills
Empathic listening and active listening both require focused attention and genuine interest to enhance communication effectiveness. To improve empathic listening, practice reflecting emotions by acknowledging feelings and validating the speaker's experience, while for active listening, use techniques like summarizing key points and asking clarifying questions to ensure understanding. Consistently avoiding distractions and maintaining eye contact are practical tips that strengthen both empathic and active listening skills.
Empathic listening vs active listening Infographic
 relationdif.com
relationdif.com